A course of treatment with checkpoint inhibitors Yervoy (ipilimumab) and Opdivo (nivolumab) for patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma is every 3 weeks for a total of four doses. Almost forty percent of patients receiving this combined regimen discontinue treatment because of immune-related adverse events. Continue reading
Tag Archives: Yervoy
Opdivo and Yervoy, the new front-line standard for poor/intermediate-risk renal cell carcinoma
The results of CheckMate 214 demonstrated that combination checkpoint immunotherapy with nivolumab (Opdivo; anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody) and ipilimumab (Yervoy; anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibody), is superior to sunitinib (Sutent; multikinase inhibitor) in the treatment of patients with newly diagnosed renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Interestingly, prior to sunitinib, another immunotherapeutic approach – interferon-alpha (IFN-α) – was the front-line treatment of choice for renal cell carcinoma, which, like melanoma, is very immune-responsive. Continue reading
New Link’s Indoximod + Keytruda looks promising in Phase 2 advanced melanoma
Indoximod + Keytruda looks promising in Phase 2 advanced melanoma
IDO (indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase) is an intracellular enzyme found in antigen presenting cells that mediates immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment. Continue reading
Recent immune checkpoint study failures do not dampen enthusiasm for the future
Immune checkpoint inhibitors are simply cancer wonder drugs about which we are learning more each day. Because they don’t work optimally in many patients and some even hyper-progress, the goal is to determine ways to expand their effectiveness to more patients. As such, the number of clinical studies with checkpoints and checkpoint combinations continues to grow.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors act by blocking the abrogating phase of the immune response that is necessary to prevent autoimmune disease – by prolonging the immune response against cancer, a more robust and prolonged immune response, which is required for effective cancer therapy, is achieved with checkpoint therapy. Continue reading
Imfinzi, the latest approved checkpoint, and checkpoint combinations
The latest checkpoint inhibitor to be approved is AstraZeneca’s Imfinzi (durvalumab), a monoclonal antibody directed against PD-L1, which is expressed on cancer cells.
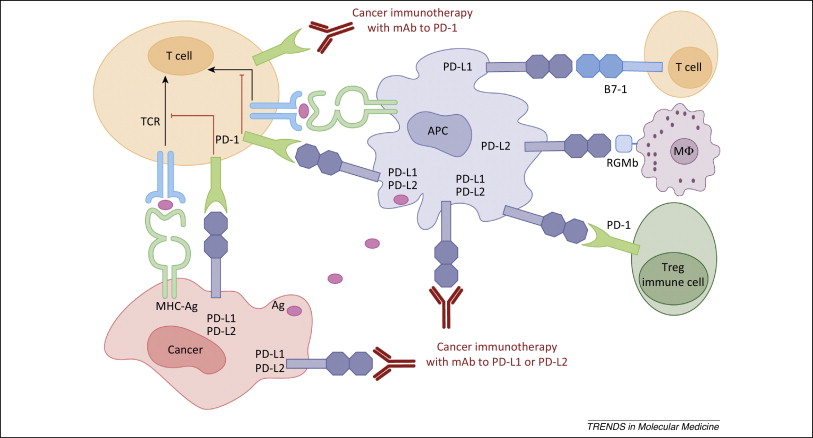
Figure 1. PD-1 / PD-L1 axis. http://www.cell.com/trends/molecular-medicine/references/S1471-4914(14)00183-X
Autoimmune toxicity on checkpoint inhibitors is associated with better responses
Cancer and autoimmune disorders are opposite sides of the same coin – cancer is a result of hypo-active immunity, whereas, autoimmune diseases is the result of hyper-active immunity. This is dramatically illustrated in examining side effects in patients with melanoma who receive checkpoint therapy with ipilimumab (Yervoy), which acts in the early stages of T-cell activation and priming, and nivolumab (Opdivo), which acts in the later stages of T-cell activation in the tumor microenvironment. Continue reading

Innate Pharma – Two NK Cell Checkpoint Inhibitors in Development
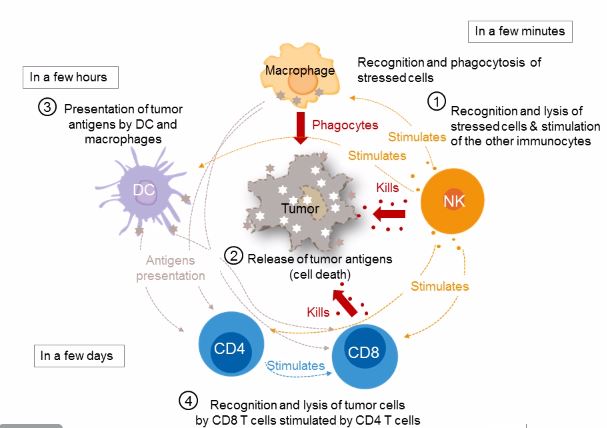
Natural Killer cells and macrophages are essential in the innate immune response to bacterial pathogens. They also provide the essential link to the adaptive immune response by presenting antigens to dendritic cells and by directly stimulating CD8+ cytotoxic T-cells.

arGENX – Immune Checkpoint Control of TNFR Superfamliy
A Dutch biotechnology company called arGENX raised $54 MM in an IPO (initial public offering) yesterday to advance its antibody pipeline. Its lead product, ARGX-110 is in late Phase 1 studies for hematologic malignancies. It is an immune checkpoint control modulator that acts on the CD70/CD27 axis, which is part of the TNFR superfamily, not the CD28/B7 superfamliy of co-stimulatory molecules. Continue reading
Two Sides of Immune Checkpoint Control
Immune checkpoint control is the hottest area in cancer immunology. Indeed, the checkpoint inhibitors have shown great activity in a variety of cancers. This article http://online.wsj.com/article/PR-CO-20140506-908279.html) summarizes 2 approaches that Merck is taking… Continue reading