Semaphorins are secreted, transmembrane, and glycosylphosphatidylinisotol-anchored glycoproteins that are important in cell to cell signaling. Humans have 20 semaphorins, the most of any species analyzed to date. Their role was originally identified in the development of the nervous system and axonal guidance. Since then, they have been shown to be important in the development and functioning of many tissues including: Continue reading
Tag Archives: avelumab
Imfinzi, the latest approved checkpoint, and checkpoint combinations
The latest checkpoint inhibitor to be approved is AstraZeneca’s Imfinzi (durvalumab), a monoclonal antibody directed against PD-L1, which is expressed on cancer cells.
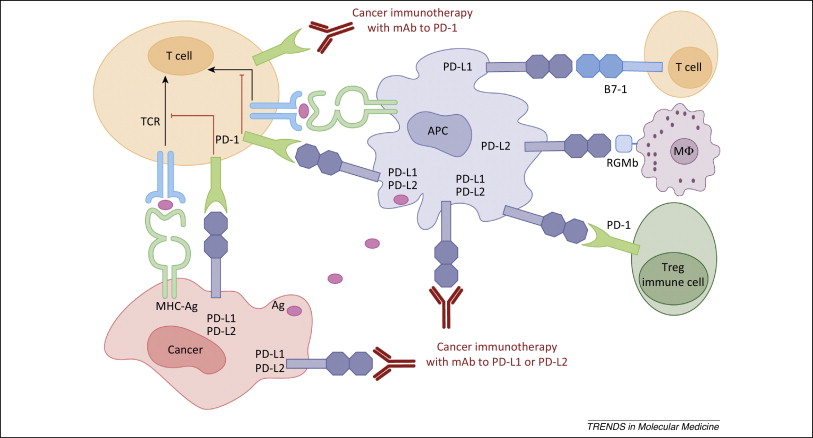
Figure 1. PD-1 / PD-L1 axis. http://www.cell.com/trends/molecular-medicine/references/S1471-4914(14)00183-X
Cancer vaccine + PD-L1 inhibitor, avelumab (Bavencio), for breast cancer
PD-L1 inhibitor, avelumab (Bavencio – Merck KGaA and Pfizer) will be combined with EpiThany’s EP-101 STEMVAC in patients with breast cancer. Avelumab was recently approved for Merckel cell carcinoma. STEMVAC is a poly-epitope DNA plasmid vaccine in the midst of a phase 1 trial of the vaccine in patients with Stage III or IV patients with breast cancer who have no evidence of disease (NED) or stable bone disease, only. The goals of the study are: Continue reading
PD-L1 Inhibitor, avelumab, approved for Merkel cell carcinoma
Avelumab (Bavencio) is a PD-L1 inhibitor that was approved for the treatment of patients with metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC). Continue reading
