We have discussed mutational burden previously on this blog – in essence, the concept is that tumors with more mutations are more visible to the immune system because the generation of new novel antigenic epitopes allows for adaptive immune responses even when previous adaptive antigen-specific immune responses have been blunted by PD-1 expression. Continue reading
Tag Archives: checkpoint
Opdivo and Yervoy, the new front-line standard for poor/intermediate-risk renal cell carcinoma
The results of CheckMate 214 demonstrated that combination checkpoint immunotherapy with nivolumab (Opdivo; anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody) and ipilimumab (Yervoy; anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibody), is superior to sunitinib (Sutent; multikinase inhibitor) in the treatment of patients with newly diagnosed renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Interestingly, prior to sunitinib, another immunotherapeutic approach – interferon-alpha (IFN-α) – was the front-line treatment of choice for renal cell carcinoma, which, like melanoma, is very immune-responsive. Continue reading
New Link’s Indoximod + Keytruda looks promising in Phase 2 advanced melanoma
Indoximod + Keytruda looks promising in Phase 2 advanced melanoma
IDO (indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase) is an intracellular enzyme found in antigen presenting cells that mediates immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment. Continue reading
Imfinzi, the latest approved checkpoint, and checkpoint combinations
The latest checkpoint inhibitor to be approved is AstraZeneca’s Imfinzi (durvalumab), a monoclonal antibody directed against PD-L1, which is expressed on cancer cells.
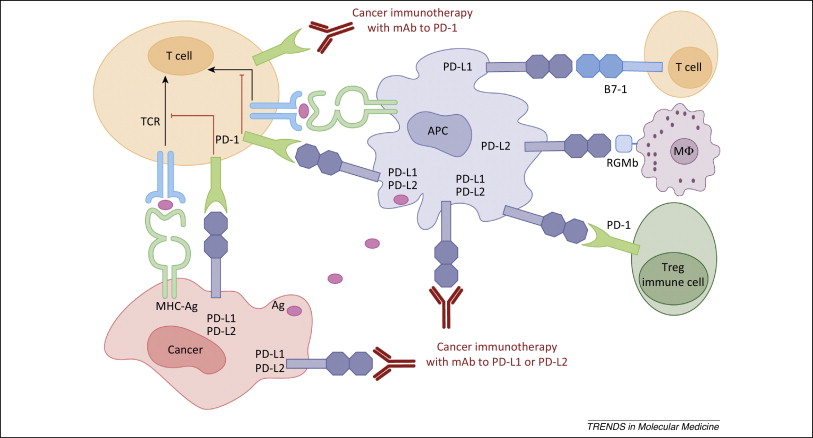
Figure 1. PD-1 / PD-L1 axis. http://www.cell.com/trends/molecular-medicine/references/S1471-4914(14)00183-X
Peripheral white blood cell profiles may predict response to checkpoint blockade
While some patients enjoy excellent and durable responses to treatment with checkpoint inhibits, most do not, and some even hyper-progress. Selecting patients who will benefit most has been challenging. Continue reading
Hyperprogression on Checkpoint Inhibition Immunotherapy
Results with checkpoint inhibitors nivolumab (PD-1, Opdivo), pembrolizumab (PD-1, Keytruda), and atezolizumab (PD-L1, Tecentriq) are impressive. Some patients have experienced incredible and prolonged responses. These drugs are truly modern medical breakthroughs.
Continue reading
Autoimmune toxicity on checkpoint inhibitors is associated with better responses
Cancer and autoimmune disorders are opposite sides of the same coin – cancer is a result of hypo-active immunity, whereas, autoimmune diseases is the result of hyper-active immunity. This is dramatically illustrated in examining side effects in patients with melanoma who receive checkpoint therapy with ipilimumab (Yervoy), which acts in the early stages of T-cell activation and priming, and nivolumab (Opdivo), which acts in the later stages of T-cell activation in the tumor microenvironment. Continue reading

Blocking CD47 Innate Checkpoint Control for Cancer Treatment
Several companies, including Trillium, Celgene, Tioma, and Forty Seven are developing products that block CD47 for the treatment of cancer. Researchers have also shown that attacking CD47 may be a better approach to bone marrow conditioning prior bone marrow transplant. Continue reading

IND for Clinical Studies of dCellVax Breast Cancer Immune Therapy Filed – Intelligent and Rational Gene Silencing Approach for Cancer
Regen Biopharma recently filed an IND (Investigational New Drug Application) with the FDA to permit the initiation of Phase 1 clinical trials of its dCellVax treatment for advanced breast cancer. Continue reading
