Olaparib (Lynparza) is a PARP (poly-ADP ribose polymerase) inhibitor that was approved by the FDA in 2014 for the treatment of patients with advanced ovarian cancer who have mutated BRCA1,2 gene. Recently, the drug showed a 70% reduction in risk of progression in patients with less-advanced disease in the maintenance therapy setting:
The Phase III SOLO-2 trial demonstrated a significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) in germline BRCA-mutated (gBRCA), platinum-sensitive, relapsed ovarian cancer patients treated with Lynparza (olaparib) tablets (300mg twice daily) compared with placebo in the maintenance setting. The trial met its primary endpoint of investigator assessed PFS (HR 0.30; 95% CI 0.22 to 0.41; P<0.0001; median 19.1 months vs 5.5 months).
PARP inhibitors act in a counter-intuitive manner – by blocking PARP in the context of mutated BRCA1, the cell becomes overwhelmed with double strand breaks, leading to crisis and cell death. BRCA1 mutations, alone, predispose the cell to the accumulation of mutations in protooncogenes and tumor suppressor genes – a few double strand breaks are tumorigenic, whereas a massive number of double strand breaks, as occurs in the context of PARP inhibition, leads to apoptosis.
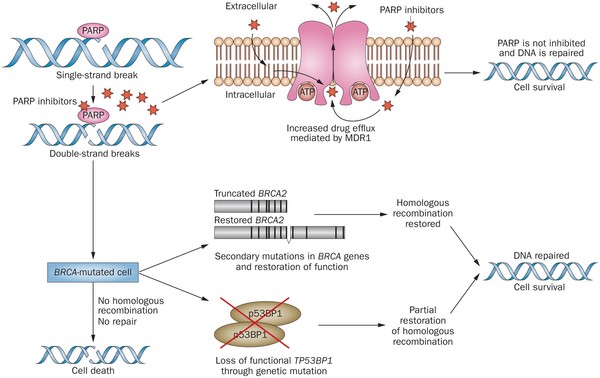
Figure 1. http://www.nature.com/nrclinonc/journal/v12/n1/full/nrclinonc.2014.163.html
The use of PARP inhibitors for breast cancer makes great sense, However, in a Phase 3 trial of velparib, an experimental PARP inhibitor, failed to achieve better rates of complete pathogenic response in patients with triple negative breast cancer (TNBC – lack of HER-2, estrogen, and progesterone receptor up-regulation) versus chemotherapy, alone.
At the ASCO conference last week, AstraZeneca presented data on the use of olaparib in 302 patients with BRCA1,2 mutated breast cancer from its OlympiAD trial that compares olaparib against physician’s choice of chemotherapy (capecitabine 2500 mg/m2 d1-14 q 21, or vinorelbine 30 mg/m2 d1,8 q 21, or eribulin 1.4 mg/m2 d1,8 q 21):
OlympiAD Inclusion Criteria:
- Germline mutation in BRCA1 or BRCA2 that is predicted to be deleterious or suspected deleterious.
- Histologically or cytologically confirmed breast cancer with evidence of metastatic disease.
- Prior therapy with an anthracycline and a taxane in either an adjuvant or metastatic setting.
- Prior platinum allowed as long as no breast cancer progression occurred on treatment or if given in adjuvant/neoadjuvant setting at least 12 months from last dose to study entry elapsed.
- ER/PR breast cancer positive patients must have received and progressed on at least one endocrine therapy (adjuvant or metastatic), or have disease that the treating physician believes to be inappropriate for endocrine therapy.
- ECOG performance status 0-1.
- Adequate bone marrow, kidney and liver function.
OlympiAD Exclusion Criteria:
- Prior treatment with PARP inhibitor.
- Patients with HER2 positive disease.
- More than 2 prior lines of chemotherapy for metastatic breast cancer.
- Untreated and/or uncontrolled brain metastases.
Results were quite impressive – this was the first study that demonstrated PARP inhibition is effective in breast cancer:
- About 60% of patients saw their tumors shrink, a hair more than double the 29% objective response rate seen in those patients on chemotherapy.
- Lynparza showed efficacy in patients with TNBC, which is more difficult to treat. AbbVie, which is developing its own PARP inhibitor called veliparib, recentlyannounced a study specifically geared to look at veliparib’s activity in triple negative breast cancer failed to show a benefit when added to chemo.
- Additionally, treatment with Lynparza improved the time to second progression or death compared to chemo,suggesting patients who relapsed after Lynparza experienced a less aggressive return of their cancers.
Astrazeneca is studying olaparib with many combinations, including a study in TNBC with PD-L1 inhibitor durvalumab and CTLA-4 inhibitor tremelimumab.