Two companies – Biontech, RNA vaccine and Neon Therapeutics, peptide vaccine – reported very positive results of neo-antigen vaccines in patients with refractory metastatic melanoma. Continue reading
Category Archives: active immunotherapy
Imfinzi, the latest approved checkpoint, and checkpoint combinations
The latest checkpoint inhibitor to be approved is AstraZeneca’s Imfinzi (durvalumab), a monoclonal antibody directed against PD-L1, which is expressed on cancer cells.
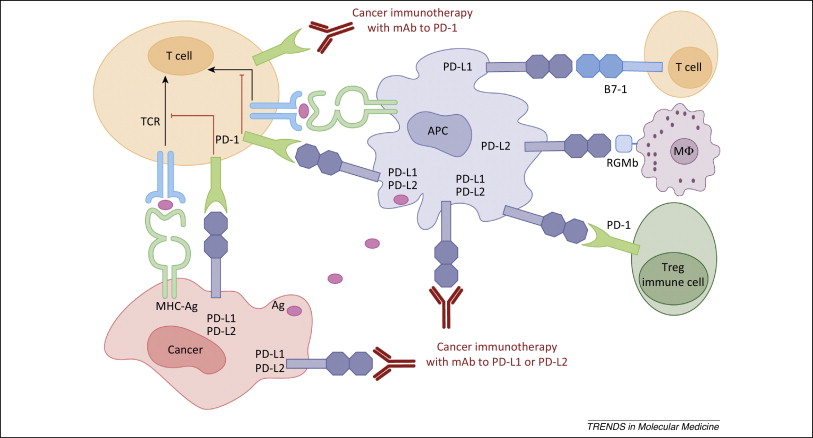
Figure 1. PD-1 / PD-L1 axis. http://www.cell.com/trends/molecular-medicine/references/S1471-4914(14)00183-X
TIGIT, a CTLA4-esque Immune Checkpoint for Cancer
Immune checkpoint-directed therapy is producing unprecedented clinical results in many patients. So much so, that the FDA recently reversed its longstanding policy or approving cancer drugs based on site of origin, to the presence of a biomarker (microsatellite instability (MSI-H) or mismatch-deficient repair (dMDR) as the indication for therapy with pembrolizumab (Ketruda), and PD-1 blocker. Cancers expressing MSI-H or dMDR mutate at a rapid rate, presenting novel epitopes to the immune system, which is readily mobilized against them so that tumor infiltrating T-cells are reliably present. Blocking the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in this context allows for prolongation of the immune response and better clinical results. Continue reading
PD-L1 Inhibitor, avelumab, approved for Merkel cell carcinoma
Avelumab (Bavencio) is a PD-L1 inhibitor that was approved for the treatment of patients with metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC). Continue reading
Hyperprogression on Checkpoint Inhibition Immunotherapy
Results with checkpoint inhibitors nivolumab (PD-1, Opdivo), pembrolizumab (PD-1, Keytruda), and atezolizumab (PD-L1, Tecentriq) are impressive. Some patients have experienced incredible and prolonged responses. These drugs are truly modern medical breakthroughs.
Continue reading
Argos’ Phase 3 Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Study Discontinued by Data Monitoring Committee
Rocapuldencel-T is an autologous dendritic cell immunotherapy for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma about which we have written previously. It is produced by isolating patient tumor mRNA, which is then electroporated into patient dendritic cells in the presence of CD40 ligand. The rationale of this approach is to bypass mechanisms by which cancer cells dampen the anti-tumor immune response, including down-regulation of MHC Class I molecules. If the cancer antigens are presented on licensed dendritic cells, logically, the immune system would be appropriately stimulated to attack the cancer. Continue reading
Interferon alpha gene therapy for refractory superficial bladder cancer in Phase III study
Valstar (valrubicin), the last drug approved for the treatment of superficial bladder cancer that is refractory to front-line therapy with BCG (bacillus Calmette-Guerin), entered the market in 1998. The registration study for Valstar demonstrated a twenty percent complete response rate three months following six weekly intravesical (transurethral administration into the bladder) instillations of the novel anthracycline in patients with BCG-refractory carcinoma in situ of the bladder. Continue reading
Autoimmune toxicity on checkpoint inhibitors is associated with better responses
Cancer and autoimmune disorders are opposite sides of the same coin – cancer is a result of hypo-active immunity, whereas, autoimmune diseases is the result of hyper-active immunity. This is dramatically illustrated in examining side effects in patients with melanoma who receive checkpoint therapy with ipilimumab (Yervoy), which acts in the early stages of T-cell activation and priming, and nivolumab (Opdivo), which acts in the later stages of T-cell activation in the tumor microenvironment. Continue reading
PD-L1 Expression correlates with outcomes in patients with melanoma
Keytruda (pembrolizumab) and Opdivo (nivolumab) are monoclonal antibodies that disrupt the PD-1 (Opdivo) / PD-L1 (Keytruda) pathway; they are approved by the FDA for the treatment of patients with unresectable melanoma, as well as other cancers including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), head and neck cancer, renal cell carcinoma (Opdivo), and Hodg kin lymphoma (Opdivo). Keytruda is limited to patients with NSCLC with a tumor proportion score (TPS) of greater than 50% for PD-L1 staining. Continue reading
Etinostat blocks Treg activity via FOXP3 suppression
Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors block the removal of acetyl groups from histone proteins. Since acetylation of histones puts chromatin in a more favorable condition for transcription, HDAC inhibitors maintain this favorable state. HDAC inhibitors have been approved for use in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. They act by sustaining transcription of tumor suppressor genes, which leads to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Continue reading
