Researches with the Ovarian Tumor Tissue Analyses Consortium analyzed the CD8+ (cytotoxic T-cell) content of tumors from 5,500 patients and compared them with clinical outcome. The analysis was large enough to allow for comparison by histologic subtype – endometrioid, clear cell, mucinous, and low-grade serous ovarian cancer, as well as high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Included in the sample were 3,200 high grade serous ovarian cancers. Continue reading
Category Archives: Therapy
Pancreatic cancer – early detection, immune response, and infection-based resistance
Approximately 1.6 percent of men and women will be diagnosed with pancreatic cancer at some point during their lifetime. In 2014, an estimated 64,668 patients were living with the disease. The five-year survival for pancreatic cancer is 8.2% and it is projected to be the second leading cause of death due to cancer (behind lung cancer) in the US by the year 2030. For good reason, then, November is Pancreatic Awareness Month. Several recent research items are of particular interest to us. Continue reading
Olaparib – PARP inhibitor for triple negative breast cancer
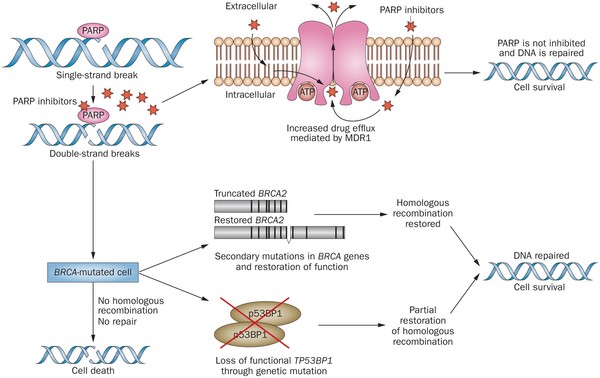
Olaparib (Lynparza) is a PARP (poly-ADP ribose polymerase) inhibitor that was approved by the FDA in 2014 for the treatment of patients with advanced ovarian cancer who have mutated BRCA1,2 gene. Recently, the drug showed a 70% reduction in risk of progression in patients with less-advanced disease in the maintenance therapy setting:
The Phase III SOLO-2 trial demonstrated a significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) in germline BRCA-mutated (gBRCA), platinum-sensitive, relapsed ovarian cancer patients treated with Lynparza (olaparib) tablets (300mg twice daily) compared with placebo in the maintenance setting. The trial met its primary endpoint of investigator assessed PFS (HR 0.30; 95% CI 0.22 to 0.41; P<0.0001; median 19.1 months vs 5.5 months).
PARP inhibitors act in a counter-intuitive manner – by blocking PARP in the context of mutated BRCA1, the cell becomes overwhelmed with double strand breaks, leading to crisis and cell death. BRCA1 mutations, alone, predispose the cell to the accumulation of mutations in protooncogenes and tumor suppressor genes – a few double strand breaks are tumorigenic, whereas a massive number of double strand breaks, as occurs in the context of PARP inhibition, leads to apoptosis.
The use of PARP inhibitors for breast cancer makes great sense, However, in a Phase 3 trial of velparib, an experimental PARP inhibitor, failed to achieve better rates of complete pathogenic response in patients with triple negative breast cancer (TNBC – lack of HER-2, estrogen, and progesterone receptor up-regulation) versus chemotherapy, alone.
At the ASCO conference last week, AstraZeneca presented data on the use of olaparib in 302 patients with BRCA1,2 mutated breast cancer from its OlympiAD trial that compares olaparib against physician’s choice of chemotherapy (capecitabine 2500 mg/m2 d1-14 q 21, or vinorelbine 30 mg/m2 d1,8 q 21, or eribulin 1.4 mg/m2 d1,8 q 21):
OlympiAD Inclusion Criteria:
- Germline mutation in BRCA1 or BRCA2 that is predicted to be deleterious or suspected deleterious.
- Histologically or cytologically confirmed breast cancer with evidence of metastatic disease.
- Prior therapy with an anthracycline and a taxane in either an adjuvant or metastatic setting.
- Prior platinum allowed as long as no breast cancer progression occurred on treatment or if given in adjuvant/neoadjuvant setting at least 12 months from last dose to study entry elapsed.
- ER/PR breast cancer positive patients must have received and progressed on at least one endocrine therapy (adjuvant or metastatic), or have disease that the treating physician believes to be inappropriate for endocrine therapy.
- ECOG performance status 0-1.
- Adequate bone marrow, kidney and liver function.
OlympiAD Exclusion Criteria:
- Prior treatment with PARP inhibitor.
- Patients with HER2 positive disease.
- More than 2 prior lines of chemotherapy for metastatic breast cancer.
- Untreated and/or uncontrolled brain metastases.
Results were quite impressive – this was the first study that demonstrated PARP inhibition is effective in breast cancer:
- About 60% of patients saw their tumors shrink, a hair more than double the 29% objective response rate seen in those patients on chemotherapy.
- Lynparza showed efficacy in patients with TNBC, which is more difficult to treat. AbbVie, which is developing its own PARP inhibitor called veliparib, recentlyannounced a study specifically geared to look at veliparib’s activity in triple negative breast cancer failed to show a benefit when added to chemo.
- Additionally, treatment with Lynparza improved the time to second progression or death compared to chemo,suggesting patients who relapsed after Lynparza experienced a less aggressive return of their cancers.
Astrazeneca is studying olaparib with many combinations, including a study in TNBC with PD-L1 inhibitor durvalumab and CTLA-4 inhibitor tremelimumab.
Interferon alpha gene therapy for refractory superficial bladder cancer in Phase III study
Valstar (valrubicin), the last drug approved for the treatment of superficial bladder cancer that is refractory to front-line therapy with BCG (bacillus Calmette-Guerin), entered the market in 1998. The registration study for Valstar demonstrated a twenty percent complete response rate three months following six weekly intravesical (transurethral administration into the bladder) instillations of the novel anthracycline in patients with BCG-refractory carcinoma in situ of the bladder. Continue reading

Hypomethylating agents are effective in myelodysplastic syndrome
Results of studies in patients with low- and intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) treated with hypomethylating agents (low dose azacytidine or decitabine) followed for a median of 18 months were presented at the Society of Hematologic Oncology meeting in Houston on September 9, 2016. Continue reading

New data with temozolomide plus radiation for brain cancers
The results of two studies have demonstrated that the use of temozolomide (TMZ) plus radiation increases disease-free and overall survival in patients with glioblastoma and a low grade glioma called anaplastic glioma. Continue reading
Rociletinib for Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with EGFR T790M Mutation – Anthony J. Meglio, Contributor
There are two major subtypes of lung cancer: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC), which accounts for 85% of all cases, and Small Cell Lung Cancer (SMLC). About 60% of NSCLC are unresectable at diagnosis, hence, the poor prognosis – ten to twelve months survival when treated with platinum-based chemotherapy. Treatment options are evaluated based on the histologic subtype and the presence of mutations to determine the the best combination of molecular therapies for treatment. Ten to twenty percent of patients with NSCLC have a mutated epidermal growth factor receptor, most commonly. a deletion in the in-frame of exon 19 (around amino acid 747 to 752) or a L858R point mutation of exon 21. On June 1, 2016, the FDA approved the first blood test (liquid biopsy) companion diagnostic to determine whether these mutations are present. Continue reading

Combined Endoglin and VEGF Monoclonal Antibody Therapy in Cancer – Subasinghe Nissanga A Dias, Contributor
Blood vessel formation (angiogenesis) is an important pathologic process in solid tumors. The liberation of vast amounts of vasoendothelial growth factor (VEGF), which attracts endothelial cells, is responsible for angiogenesis. Continue reading

FDA Grants Antibody-Drug Conjugate Breakthrough Designation in Triple Negative Breast Cancer – Amani Khawatmi, Contributor
The FDA granted Breakthrough Therapy Designation to Sacituzumab govetican (IMMU-132) for treatment of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). A diagnosis of triple negative breast cancer means that the three most common types of receptors known to fuel most breast cancer growth–estrogen, progesterone, and the HER-2/neu gene– are not present in the cancer tumor. This means that the breast cancer cells have tested negative for hormone epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER-2), estrogen receptors (ER), and progesterone receptors (PR). Since the tumor cells lack the necessary receptors, common treatments likehormone therapy and drugs that target estrogen, progesterone, and HER-2 are ineffective.

Vanquish Oncology – Procaspase 3 Activation Factor to Selectively Induce Apoptosis
Procaspase-3 is an executioner protein catalyzes the hydrolysis of more than 100 protein targets. These cleavage events ultimately lead to cell suicide, or apoptosis. Caspase-3 is triggered by the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis cascades. Continue reading