The FDA granted approval of axicabtagene ciloleucel (YESCARTA) on October 25, 2017, two months following the approval of tisagenlecleucel (KYMRIAH) – both are anti-CD19-directed CAR T (chimeric antigen receptor T-cell) therapies that employ re-programmed autologous T-cells to fight cancer:
- KYMRIAH is indicated for B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) that is refractory or in second or later relapse;
- YESCARTA is indicated for use in patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma after two or more lines of systemic therapy, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL – the most common form of NHL – non-Hodgkin lymphoma), primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma, high grade B-cell lymphoma, and DLBCL arising from follicular lymphoma.

Figure 1. The engineered receptor on CAR T cells binds to an antigen on cancer cells. After binding, components of the receptor inside the T cell provide signals that activate it.
Credit: Kite Pharma https://www.cancer.gov/news-events/cancer-currents-blog/2017/yescarta-fda-lymphoma.
The CAR T therapies are comprised of autologous T cells that are genetically modified using a lentiviral vector to encode an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR). To prepare YESCARTA, a patient’s own T cells are harvested and genetically modified ex vivo by retroviral transduction to express a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) comprising a murine anti-CD19 single chain variable fragment (scFv) linked to CD28 and CD3-zeta co-stimulatory domains. The anti-CD19 CAR T cells are expanded and infused back into the patient, where they can recognize and eliminate CD19-expressing target cells. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/BiologicsBloodVaccines/CellularGeneTherapyProducts/ApprovedProducts/UCM581226.pdf.
KYMRIAH is comprised of autologous T cells that are genetically modified using a lentiviral vector to encode an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR). The CAR is comprised of a murine single-chain antibody fragment (scFv) specific for CD19, followed by a CD8 hinge and transmembrane region that is fused to the intracellular signaling domains for 4-1BB (CD137) and CD3 zeta. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/BiologicsBloodVaccines/CellularGeneTherapyProducts/ApprovedProducts/UCM573941.pdf
YESCARTA – B-cell Lymphoma
The registration trial (ZUMA-1) for YESCARTA was a single-arm, open label study of 101 patients with relapsed or refractory aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Eligible patients had refractory disease to the most recent therapy or relapse within 1 year after autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Half of the patients (51%) had a complete response, that is, their cancers disappeared completely.
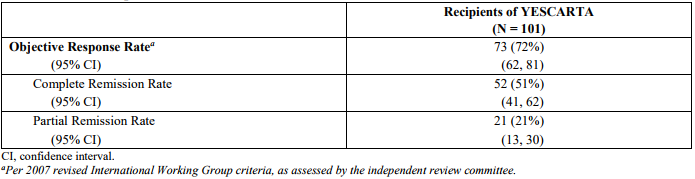
Table 1. Response rates on ZUMA-1. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/BiologicsBloodVaccines/CellularGeneTherapyProducts/ApprovedProducts/UCM581226.pdf
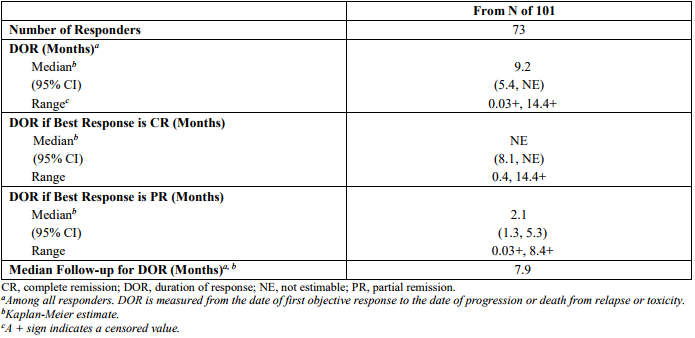
Table 2. Durability of response on ZUMA-1. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/BiologicsBloodVaccines/CellularGeneTherapyProducts/ApprovedProducts/UCM581226.pdf
Standard of care in refractory B-cell lymphomas
SCHOLAR-1 is a study of patients with DLBCL that pooled the outcomes from two previously conducted randomized trials and databases from two large academic cancer centers:
SCHOLAR-1 pooled data from 2 phase 3 clinical trials (Lymphoma Academic Research Organization-CORAL and Canadian Cancer Trials Group LY.12) and 2 observational cohorts (MD Anderson Cancer Center and University of Iowa/Mayo Clinic Lymphoma Specialized Program of Research Excellence). SCHOLAR-1 is the largest patient-level pooled retrospective analysis that characterizes response rates and survival for a population of patients with refractory DLBCL.
The objective response rate was 26% with 7% of patients achieving complete responses to the next line of therapy; the median overall survival was 6.3 months. Twenty percent of patients were alive at 2-years.
YESCARTA vs standard of care
There are no randomized studies comparing YESCARTA to standard of care therapies in refractory DLBCL. However, using the results of ZUMA-1 and SCHOLAR-1, Neelapu and colleagues compared the efficacy of the treatments, adjusting for imbalances and key covariates.
The patients in the two studies were balanced for distribution of sex, disease type, and the proportion of patients with disease refractory to two consecutive lines of therapy. ZUMA-1 included more patients with three or more prior lines of therapy, with advanced, stage III-IV disease and less favorable International Prognostic Index scores. Also, more patients in ZUMA-1 had transformed follicular lymphoma or primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma, and more patients in SCHOLAR-1 had primary refractory disease.
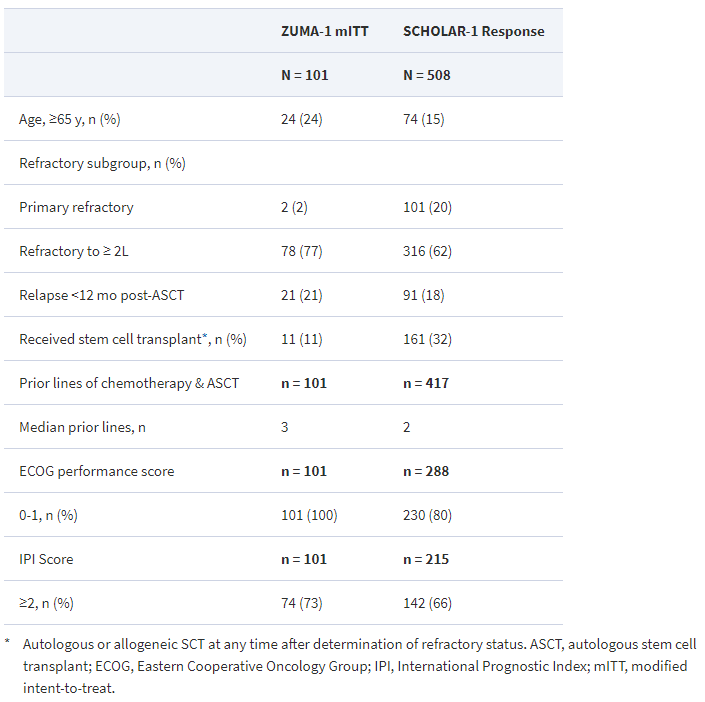
Table 3. Patient characteristics – ZUMA-1 versus SCHOLAR-1. https://academic.oup.com/annonc/article/28/suppl_5/mdx376.026/4109240
The risk of death in ZUMA-1 was reduced by 77% relative to SCHOLAR-1 (p < 0.0001). Moreover, YESCARTA
“induced remissions that last years in a significant proportion of patients, suggesting the possibility of cures in these patients, who typically do not survive beyond six months,” said Neelapu.
