The National Cancer Institute has a very informative, yet easy to understand overview presented as a Q&A – Targeted Cancer Therapies.
Among the interesting and informative facts is a discussion about side effects. The thinking is that by targeting very specific pathways in the cell that are over-expressed in cancer, the side effects of targeted therapies would be significantly lower than those seen with traditional chemotherapy. This is generally true, however, targeted therapies are not without side effects. Diarrhea and inflammation of the liver (hepatitis) are common, as are acneiform rashes, clotting and would healing problems, and high blood pressure. Interestingly, in patients receiving signal transduction inhibitors of the epidermal growth factor receptor (Tarceva and Iressa), an acneiform rash is correlated with a better response than patients who do not develop the rash. The same is true for hypertension associated with Avastin, a monoclonal antibody that binds to VEGF to block angiogenesis.
The list of targeted therapies approved by the FDA is getting longer all the time. Some are limited to patients with a specific mutation, and the labels of the compounds restrict use to patients whose tumors exhibit the specific mutations (for example, Gleevec for patients with Philadelphia chromosome positive myeloid leukemia and Xalkori for patients with lung cancers that express the mutated ALK gene). Others are for use in cancers that either over-express oncogenic molecules (Herceptin and Kadcyla for HER-2+ breast cancer), are driven by specific growth factors (Xtandi for prostate cancer, which blocks androgens from binding to the nuclear receptor, as well as the translocation of the AR to the nucleus and its interaction with DNA), or pathways known to be specifically associated with certain cancers (Erivedge for advanced basal cell carcinoma).
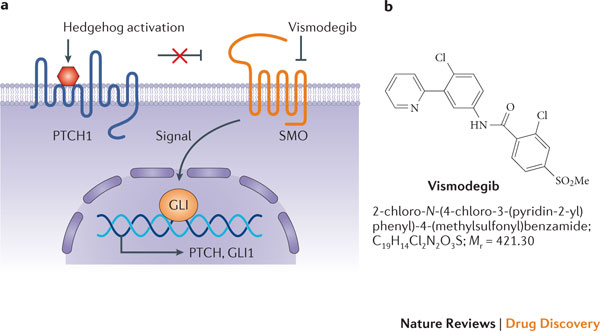
Vismodegib (Erivedge) interferes with the Hedgehog pathway. The Patched (12 membrane-spanning receptor protein) normally disables Smoothened (7 membrane-spanning protein) rendering it functionally inert. This maintains transcription factor Gli in a cleaved state, acting as a transcriptional repressor. When Hedgehog proteins bind to Patched, Smoothened is released and protects Gli from cleavage. Uncleaved Gli travels to the nucleus and is an inducer of transcription, increasing Cyclin D1 and stimulating the cell cycle (proliferation). Vismodegib blocks the actions of Smoothened.
Adenocarcinoma of the stomach or gastroesophageal junction: Trastuzumab (Herceptin®)
Basal cell carcinoma: Vismodegib (Erivedge™)
Brain cancer: Bevacizumab (Avastin®), Everolimus (Afinitor®)
Breast cancer: Everolimus (Afinitor®), tamoxifen, toremifene (Fareston®), Trastuzumab (Herceptin®), fulvestrant (Faslodex®), anastrozole (Arimidex®), exemestane (Aromasin®), lapatinib (Tykerb®), letrozole (Femara®), pertuzumab (Perjeta™),ado-trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla™)
Colorectal cancer: Cetuximab (Erbitux®), Panitumumab (Vectibix®), Bevacizumab (Avastin®), Ziv-aflibercept (Zaltrap®), Regorafenib (Stivarga®)
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: Imatinib mesylate (Gleevec®)
Head and neck cancer: Cetuximab (Erbitux®)
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor: Imatinib mesylate (Gleevec®), Sunitinib (Sutent®), Regorafenib (Stivarga®)
Giant cell tumor of the bone: Denosumab (Xgeva®)
Kaposi sarcoma: Alitretinoin (Panretin®)
Kidney cancer: Bevacizumab (Avastin®), Sorafenib (Nexavar®), Sunitinib (Sutent®), Pazopanib (Votrient®), Temsirolimus (Torisel®), Everolimus (Afinitor®), Axitinib (Inlyta®)
Leukemia: Tretinoin (Vesanoid®), Imatinib mesylate (Gleevec®), Dasatinib (Sprycel®), Nilotinib (Tasigna®), Bosutinib (Bosulif®), Rituximab (Rituxan®), Alemtuzumab (Campath®), Ofatumumab (Arzerra®), Obinutuzumab (Gazyva™), Ibrutinib (Imbruvica™), Idelalisib (Zydelig®)
Liver cancer: Sorafenib (Nexavar®)
Lung cancer: Bevacizumab (Avastin®), Crizotinib (Xalkori®), Erlotinib (Tarceva®), Gefitinib (Iressa®), Afatinib dimaleate (Gilotrif®), Ceritinib (LDK378/Zykadia)
Lymphoma: Tositumomab and 131I-tositumomab (Bexxar®), Ibritumomab tiuxetan (Zevalin®), Denileukin diftitox (Ontak®), Brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris®), Rituximab (Rituxan®), Vorinostat (Zolinza®), Romidepsin (Istodax®), Bexarotene (Targretin®), Bortezomib (Velcade®), Pralatrexate (Folotyn®), Lenaliomide (Revlimid®), Ibrutinib (Imbruvica™), Siltuximab (Sylvant™), Idelalisib (Zydelig®), Belinostat (Beleodaq™)
Melanoma: Ipilimumab (Yervoy®), Vemurafenib (Zelboraf®), Trametinib (Mekinist®), Dabrafenib (Tafinlar®)
Multiple myeloma: Bortezomib (Velcade®), Carfilzomib (Kyprolis®), Lenaliomide (Revlimid®), Pomalidomide (Pomalyst®)
Myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative disorders: Imatinib mesylate (Gleevec®)
Pancreatic cancer: Erlotinib (Tarceva®), Everolimus (Afinitor®), Sunitinib (Sutent®)
Prostate cancer: Cabazitaxel (Jevtana®), Enzalutamide (Xtandi®), Abiraterone acetate (Zytiga®), Radium 223 chloride (Xofigo®)
Soft tissue sarcoma: Pazopanib (Votrient®)
Stomach cancer: Ramucirumab (Cyramza™)
Systemic mastocytosis: Imatinib mesylate (Gleevec®)
Thyroid cancer: Cabozantinib (Cometriq™), Vandetanib (Caprelsa®), Sorafenib (Nexavar®)