The combination of Herceptin plus pan-HER (EGFR and Her 2 an 4) kinase inhibitor neratinib resulted in a 33% improvement in progression free survival versus Herceptin alone in breast cancer patients. Rituxan combined with idelalisib, PI3K inhibitor, resulted in a near doubling of progression-free survival at 24 weeks versus Rituxan, alone in patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia, non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, and small cell lymphoma. The news for neratinib tripled the valuation of Puma Biotechnology, while the FDA granted approval of Gilead’s drug Zydelig (idelalisib).
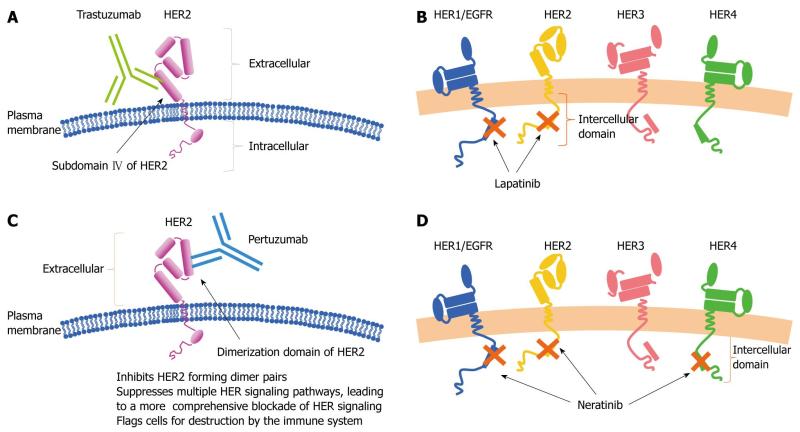
Combination therapy is the mainstay of cancer treatment, and so the axiom is proved once again with these two examples. Herceptin (trastuzumab) acts by binding to the HER2 extracellular domain and blocking HER-2’s ability to dimerize with other HER receptors, thereby blocking downstream signaling. Combining Herceptin with tyrosine kinase inhibitors would ostensibly result in a more complete shut down of signaling from the HER-family tyrosine kinase receptors. [Binding of Herceptin also induces ADCC (antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity).]
Lapatinib (Tykerb) is an irreversible inhibitor of the the EGFR (ErbB1) and Her-2/neu (ErbB2) receptor tyrosine kinases. It is approved for use in patients with Her-2+ breast cancer who have failed treatment with an anthracycline, taxane, and trastuzumab (Herceptin), Neratinib is an IRREVERSIBLE inhibitor of EGRF, Her-2, and Her-4 receptor kinases. Neratinib is associated with severe diarrhea, however.
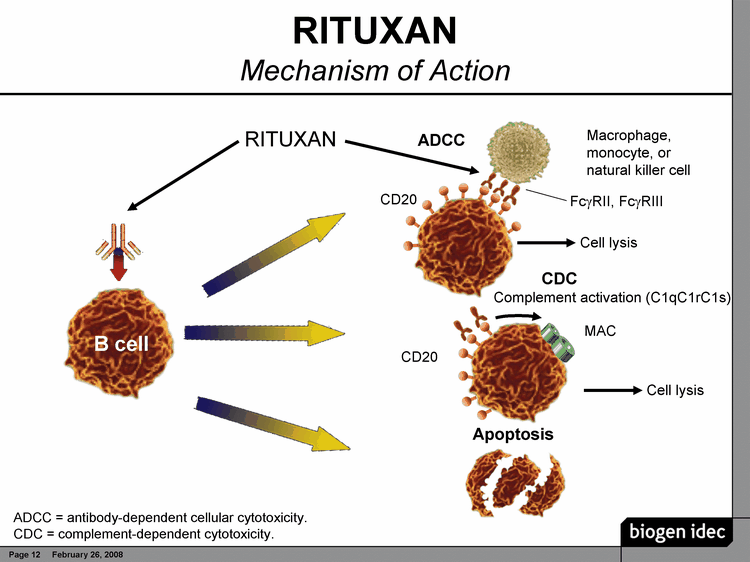
Rituxan is a monoclonal antibody against the CD20 B-cell antigen. It opsonizes B-cells for antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). Rituxan does not bind to a receptor tyrosine kinase, therefore, it does not block mitogenic signaling.
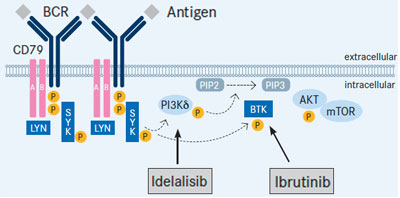
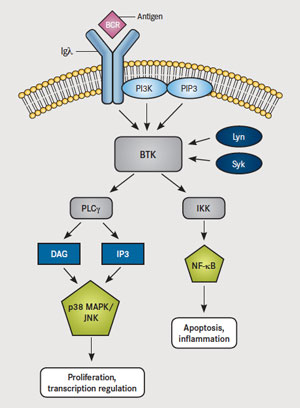
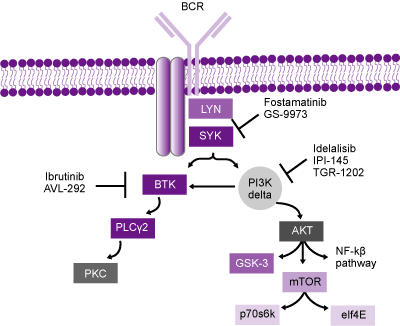
Idelalisib (Zydelig) blocks PI3K, a central molecule in the Ras oncogenic pathway that leads to Akt/PKB activation. Ibrutinib (Imbruvica) is a drug that blocks Bruton’s kinase (BTK), which is downstream of PI3K – it is approved for use in Mantle Cell Lymphoma and Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. BTK triggers the PLCγ and DAG pathways that result in PKC induction and subsequent triggering of IKK (NFκB) and MAPK (Fos and Jun) – these actions lead to proliferation and blocking of apoptosis. (NFκB induces anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and IAPs – inhibitors of apoptosis, as well as pro-inflammatory molecules COX-2 and TNF. MAPK leads to induction of Erk transcription factors and AP-1, which induces cyclin D-1 leading to proliferation.)
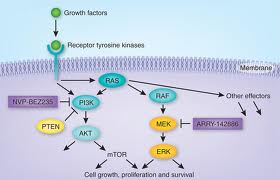
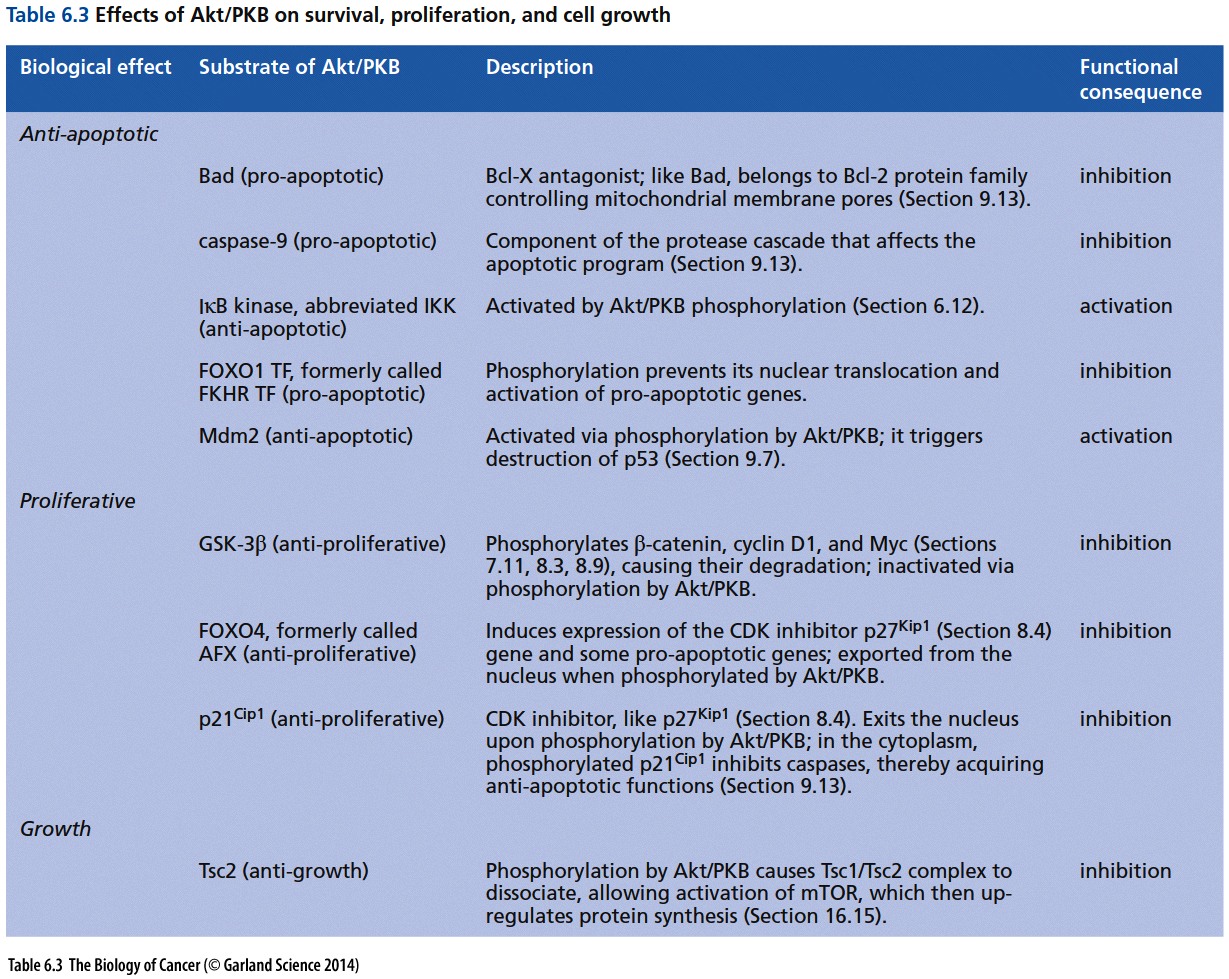
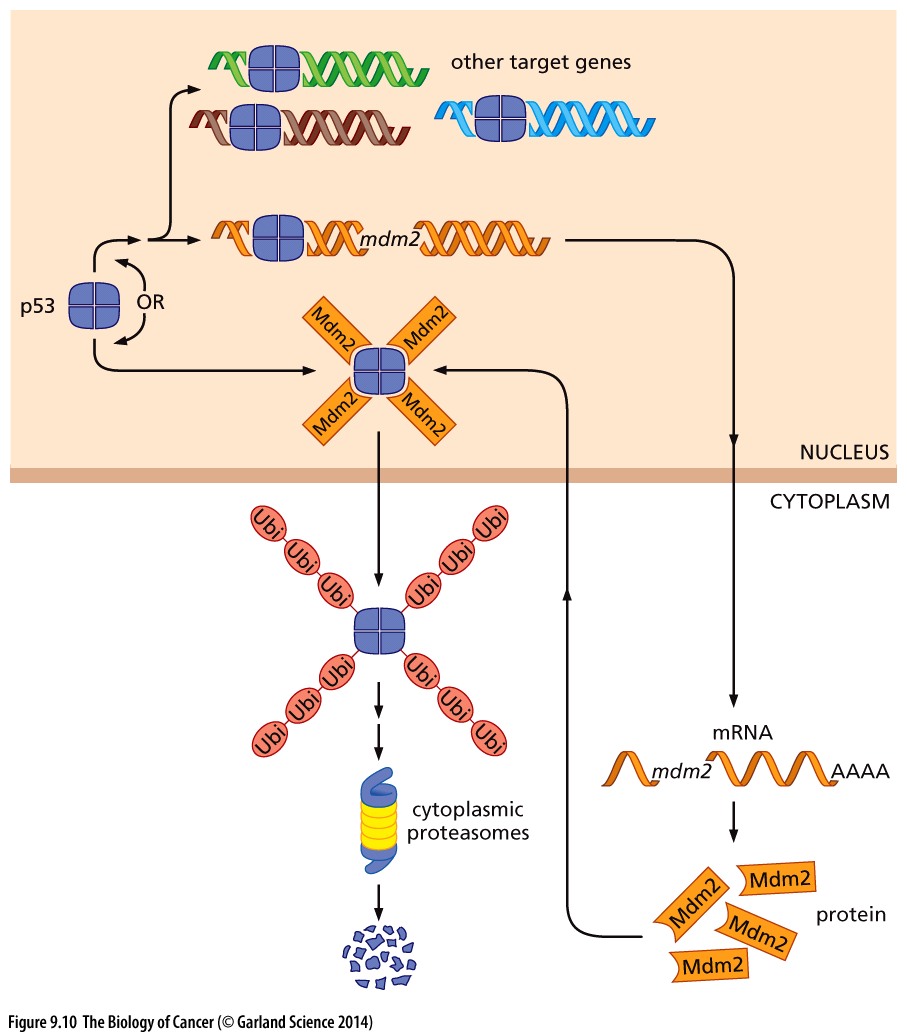
PI3K is one of the Ras effector molecules. It activates Akt/PKB, a crucial molecule that blocks apoptosis (via inhibition of Mdm2, Bad, Caspase 9, and induction of IKK) and drives proliferation – see figures, below (Copyright 2014 from The Biology of Cancer, 2nd Ed. by Weinberg. Reproduced by permission of Garland Science/Taylor & Francis LLC). By inducing Mdm2, which binds to p53, Akt/PKB blocks apoptosis.
As if that weren’t enough to help drive malignant transformation, additionally, Akt/PKB induces the expression of myc, which further drives proliferation by:
- Inducing Id proteins that bind pRb
- Inhibiting bHLH proteins that drive differentiation
- Inducing E2F1-3,
- Blocking CDK inhibitors (p15, p21, and p27),
- Induces Culi1 (which degrades p27).
Addtionally, myc induces hTERT, which is required for immortalization. So, Akt/PKB is responsible for the induction of many molecules that are required to transform and maintain cancer cells.
It will be interesting to see how Imbruvica (Bruton’s Kinase inhibitor) compares to Zydelig (idelalisib) in B cell lymphomas and leukemia given the biology of BTK and PI3K.