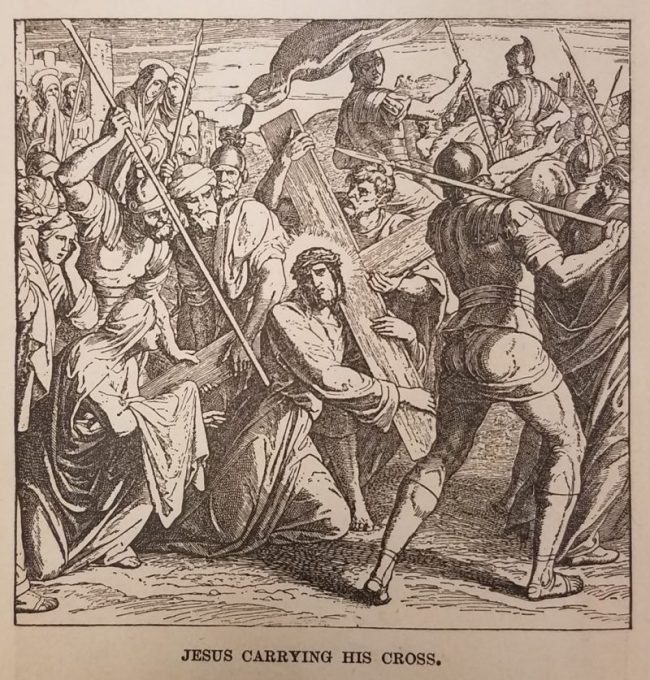
Image: The Holy Family by Sc. Muller from The Holy Bible, The Latin Vulgate Revised with Annotations by The Right Rev. R. Challoner D.D.
New York: Thomas Kelly, Publisher, 1879.
Courtesy of Archives and Special Collections
YEAR OF ST. JOSEPH
“I do not remember even now that I have ever asked anything of [St. Joseph] which he has failed to grant… To other saints the Lord seems to have given grace to succor us in some of our necessities, but of this glorious saint my experience is that he succors us in them all…”[1]
This year we celebrate the 150th anniversary of Pope Pius IX’s declaration of Saint Joseph as the patron saint of the Universal Church in 1870. To mark this occasion, Pope Francis proclaimed a special “Year of St. Joseph,” which began on the observance of the Solemnity of the Immaculate Conception on December 8, 2020 and will conclude on this same feast day in 2021.[2] Additionally, the annual Feast of Saint Joseph is celebrated at this time of year. Veneration of Saint Joseph began in ancient Egypt, though Pope Sixtus IV officially recognized this custom around 1479.[3]
Saint Joseph is revered as a loving and tender father to Jesus and protector of Mary. Called by God to serve the mission of Jesus, he “cooperated… in the great mystery of Redemption,” as Saint John Paul II said, “and is truly a minister of salvation.” He encourages us to accept and welcome others as they are, and to show special concern for the disadvantaged.[4] Joseph’s compassionate nature is expressed in the above engraving by Sc. Muller in The Holy Bible, published in 1879 by Thomas Kelly Publishers, just nine years after Saint Joseph achieved sainthood. Prior to the 19th century, iconography of the Holy Family would often depict Joseph in the background, shrouded in shadows. After Joseph’s elevation to sainthood, portrayals of the Holy Family included him as an integral part of the subject and composition – as shown in Muller’s interpretation.[5] Saint Joseph’s attributes are the lily and spikenard, an aromatic oil.[6]

Saint Joseph is the patron of tradesmen and workers, travelers and refugees, the persecuted, families and homes, purity and interior life, engaged couples, people in distress due to insecurity related to food, home or clothing, as well as sickness, the poor, aged and dying.[7] On his feast day, many attend church services in his honor. Cultures throughout the world celebrate Saint Joseph’s feast day in a variety of ways. In Spain and Portugal, the Solemnity of Saint Joseph coincides with Father’s Day, generating visits to fathers and father figures. In some areas, traditional observances include the wearing of special richly colored outfits which might be worn to a parade in Saint Joseph’s honor. In the coastal city of Valencia, Spain, people make elaborate, publicly displayed papier-mâché scenes which are then burned to the ground in a celebration of creativity, mortality and rebirth known as Las Fallas.[8] Sicily has its own rich traditions for the Saint Joseph’s Feast Day. In Palermo, people organize huge bonfires known as “Vampa” in the city’s piazzas. Many towns organize moving processions accompanied by the singing of prayers and songs. Sicilians also set a Saint Joseph’s table, an altar with special foods, flowers and devotional objects to praise and give thanks.[9] Polish families set up a Saint Joseph’s table decorated with red and white to symbolize both their country and Saint Joseph. These tables include holy cards and candles, as well as meatless foods in observance of Lent. Polish hymns are also recited.[10] Some in the Philippines maintain ritual banquet customs in which community members are chosen as representatives of Saint Joseph, the Blessed Virgin Mary and the Child Jesus. The three participants are fed an opulent feast during which hymns are sung.[11] Contemporaneous celebrations in the Philippines are more overtly altruistic, and include volunteering to feed the poor, homeless and the hungry.[12]
In his recent Apostolic Letter, Patris corde (“with a father’s heart”), Pope

Francis characterizes Saint Joseph as “a beloved father, a tender and loving father, an obedient father, an accepting father; a father who is creatively courageous, a working father, a father in the shadows.” On the occasion of this Saint Joseph Feast Year, Pope Francis urges us to see the importance of “ordinary” people who, though far from the limelight, exercise patience and offer hope every day. In this, they resemble Saint Joseph, “the man who goes unnoticed, a daily, discreet and hidden presence,” who nonetheless played “an incomparable role in the history of salvation.”[13] Pope Francis’ letter concludes with a prayer to Saint Joseph, which he encourages us to pray together:
Hail, Guardian of the Redeemer,
Spouse of the Blessed Virgin Mary.
To you God entrusted his only Son;
in you Mary placed her trust;
with you Christ became man.
Blessed Joseph, to us too,
show yourself a father
and guide us in the path of life.
Obtain for us grace, mercy, and courage,
and defend us from every evil. Amen.
The images and materials shown here are but a small part of the vast patrimony available to students, faculty and researchers. For access to this or other objects in our collections, complete a research request form to set up an appointment or contact us at 973-761-9476.
[1] Teresa, and E. Allison Peers. Autobiography of St. Teresa of Avila. Mineola, NY: Dover Publications, 2010.
[2] https://www.vaticannews.va/en/pope/news/2020-12/pope-francis-proclaims-year-of-st-joseph.html, accessed 3/9/2021.
[3] https://www.britannica.com/biography/Saint-Joseph, accessed 3/9/2021.
[4] https://www.vaticannews.va/en/pope/news/2020-12/pope-francis-proclaims-year-of-st-joseph.html, accessed 3/9/2021.
[5] https://www.christianiconography.info/holyFamily.html, accessed 3/9/2021.
[6]https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saint_Joseph#:~:text=Joseph%20is%20venerated%20as%20Saint,associated%20with%20various%20feast%20days, accessed 3/9/2021.
[7] https://www.catholicculture.org/culture/liturgicalyear/activities/view.cfm?id=1050, accessed 3/9/2021.
[8] https://www.worldtravelguide.net/features/feature/las-fallas-burning-valencia-to-the-ground/, accessed 3/9/2021.
[9] https://www.scent-of-sicily.com/news/st-josephs-day-traditions-in-sicily/, accessed 3/9/2021.
[10] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saint_Joseph%27s_Day, accessed 3/9/2021.
[11] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saint_Joseph%27s_Day, accessed 3/9/2021.
[12] http://www.asianews.it/news-en/Manila:-feast-day-of-St-Joseph-for-the-poor-33765.html, accessed 3/9/2021.
[13] https://www.vaticannews.va/en/pope/news/2020-12/pope-francis-proclaims-year-of-st-joseph.html, accessed 3/9/2021.


























 The invitation to “Ike” was a logical idea since it was a major anniversary celebration for the institution, but the Deputy White House Chief of Staff and Appointments Secretary to President Eisenhower was noted lawyer, Mr. Bernard Shanley, a native of Newark who served in this capacity from 1955-57 and had established ties to Seton Hall and the Archdiocese. Ike was also connected to the values of higher education as the former President of Columbia University (1948-53) along with his prestige as a war hero and leader of the country all made for the hope that he would be a part of this anniversary pageant. However, President Eisenhower would ultimately send his regrets via telegram that he could not attend ceremonies in South Orange that year.
The invitation to “Ike” was a logical idea since it was a major anniversary celebration for the institution, but the Deputy White House Chief of Staff and Appointments Secretary to President Eisenhower was noted lawyer, Mr. Bernard Shanley, a native of Newark who served in this capacity from 1955-57 and had established ties to Seton Hall and the Archdiocese. Ike was also connected to the values of higher education as the former President of Columbia University (1948-53) along with his prestige as a war hero and leader of the country all made for the hope that he would be a part of this anniversary pageant. However, President Eisenhower would ultimately send his regrets via telegram that he could not attend ceremonies in South Orange that year.