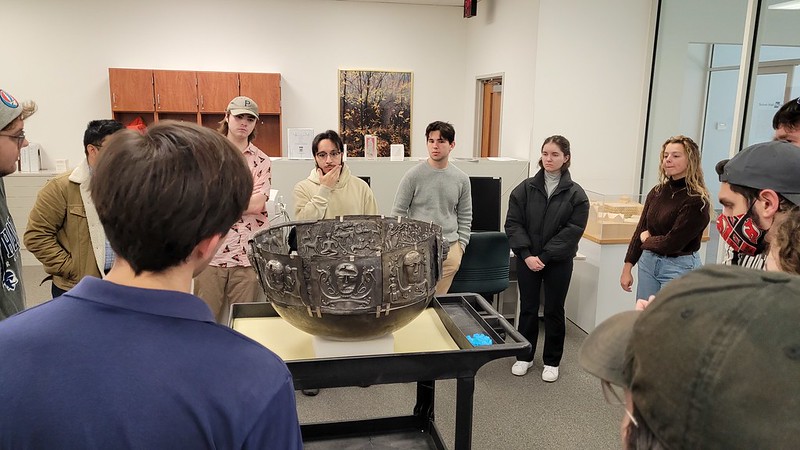
Students in Dr. Laura Wangerin's "VIKINGS!" class discuss a replica of the Gundestrup Cauldron from the university's collections
This semester, students experienced history first-hand through object-based learning (OBL), an approach that adds value to classroom studies. In OBL, students learn via engaging in conversation and discourse using artworks, artifacts, archival materials, or digital representations of unique objects as catalysts to foster a sense of wonder, awe and curiosity. Object-based learning prioritizes critical thinking inspired by close observation to connect objects to concepts learned in the classroom.
Dr. Laura Wangerin’s “VIKINGS!” class visited the Archives and Special Collections recently to view the university’s replicas of the Gundestrup Cauldron and Book of Kells in a conversation guided by the student’s thoughts, questions and observations – relating the imagery back to what was learned through readings and coursework. Students were taken by the scale of the work, the construction of the cauldron, and the high relief imagery which is visible 360 degrees around. Engaging objects via the senses connects students to the past while making connections to the present. Objects are powerful tools for learning, especially when students realize they are standing in the presence of an object made by people or cultures from long ago. In this sense, objects can become almost like time machines, bringing us back to pivotal moments in human or natural history.
Noticias Summarias das Perseguições da missam de Cochinchina, principiada, & continuada pelos Padres da Companhia de Jesu. (OCLC #: 16077971)
In Dr. Kirsten Schultz’s course “Religion and Society in Early Latin America” students visited to see rare books published around the time of the Counter-Reformation to enhance their understanding and appreciation of the issues at stake as they discussed the role of the Church in colonial society. Conversation centered on the adventencia pages of the “Noticias Summarias,” which served as an agreement that the book could be published. The volume is an important account of the Portuguese mission in Cochinchina and Tonkin, today’s Vietnam.
The Walsh Gallery and Archives and Special Collections care for the university’s various collections and make them available for study, research, exhibitions and related programs. Objects include materials from world cultures and span from the neolithic era to the present. Highlights of the collection include Byzantine and Greco-Roman coins and artifacts; Native American basketry, ceramics and beaded crafts along with tools and leather goods; Japanese toys and 19th century woodblock prints; 3,000-year-old Chinese ceramics and metalwork; contemporary Chinese art; 17th and 18th century European engravings; and documents dating to the founding of the Newark Diocese and Seton Hall College. There are also significant collections from New Jersey politicians such as Brendan Byrne – the state’s 47th governor and Donald M. Payne, New Jersey’s U.S. representative who served the 10th congressional district from 1989 until his death in 2012.
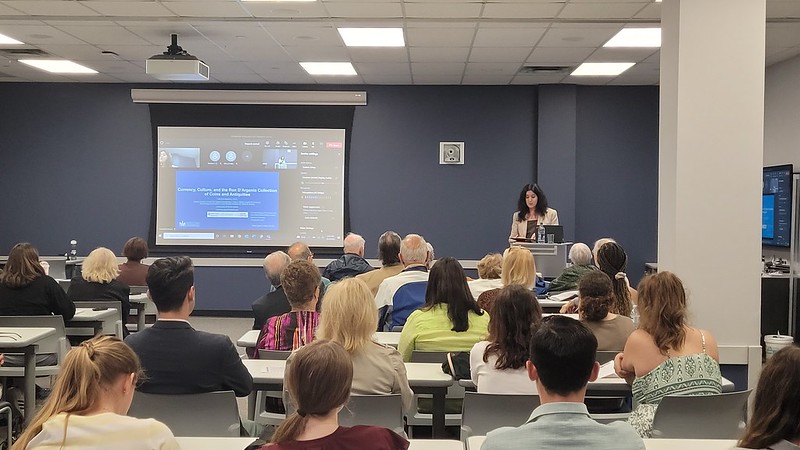
A portion of the university’s collections can be viewed on Google Arts and Culture and you can view scholar Dr. Caterina Agostini’s recent digital exhibition, “Currency Culture” which uses coins from the Ron D’Argenio Collection of Coins and Antiquities to discuss notions of power and politics as conveyed on minted coins from the Byzantine and Roman Empires.

Those interested in viewing the Gundestrup Cauldron can view it through the end of the semester on the first floor of the Walsh Library in the display windows outside the Archives and Special Collections. If you would like to make an appointment to use the collections for research, class visits or other scholarly pursuits, please contact us. We would love to hear about your projects and how we can work together to illustrate your ideas!
______
The Walsh Gallery has a considerable collection of fine art, artifacts and archeological specimens for use by faculty, students and researchers. For access to this or other objects in our collections, contact us at 973-275-2033 or walshgallery@shu.edu to make a research appointment. Now on view in the Walsh Gallery: Seton Hall Re/Collects through Friday, December 9th. The gallery is located on the 1st floor of the Walsh Library and is open Monday to Friday from 9am to 5pm. Groups of 8 or more must make an appointment prior to visiting.