I attended the Rexahn presentation at the Biotech Showcase on January 12-14, 2015. The company has 3 novel anti-cancer products in the clinic.
Archexin
The most advanced product is an anti-sense oligonucleotide that targets Akt-1, which, when phosphorylated, provides signals to many pathways resulting in (1) cellular proliferation by blocking GSK-3β (myc, β-catenin, and cyclin-D1 are induced) and blocking p21 (which inhibits cyclin E, A, and B); (2) blocking of apoptosis by inhibiting Bad and Caspase 9 and inducing NFkB (which induces IAP proteins – inhibitors of apoptosis), and by inducing Mdm2, which destroys p53; and (3) increased protein synthesis via mTOR activation. Increased Akt1 activity is thought to be responsible for everolimus (mTOR inhibitor, Afinitor) resistance.
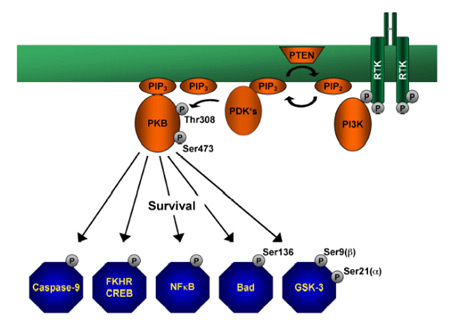
Akt1 is involved in cellular survival pathways, by inhibiting apoptotic processes. Akt1 is also able to induce protein synthesis pathways, and is therefore a key signaling protein in the cellular pathways that lead to skeletal muscle hypertrophy, and general tissue growth. Since it can block apoptosis, and thereby promote cell survival, Akt1 has been implicated as a major factor in many types of cancer. http://reader.roodo.com/mona_space/archives/8343193.html
A Phase I/II Dose-Finding, Safety and Efficacy Study of Archexin Plus Everolimus (mTOR blocker) in Metastatic Renal Cell Cancer is currently underway. The drug is administered in a dose up to 250mg/m^2/day as a continuous infusion for a cycle of 21 days (14 days infused followed by 7 days off) for up to 8 cycles.
Supinoxin
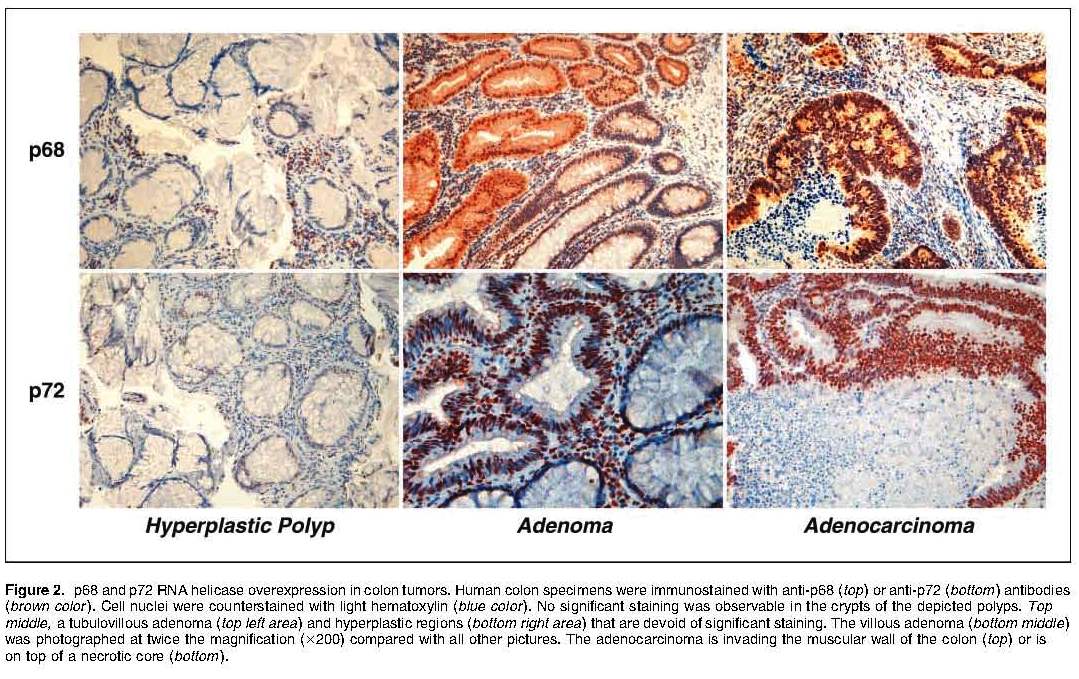
Supinoxin (RX-5902) is an orally administered, first-in-class, small molecule inhibitor of phosphorylated-p68 (P-p68). P-p68, which is selectively expressed in cancer cells and is absent in normal tissue, increases the activity of multiple cancer related genes including cyclin D1, c-jun and c-myc, and plays a role in tumor progression and metastasis. Over-expression of P-p68 has been observed in solid tumors, such as melanoma, colon, ovarian and lung.
p68 RNA helicase is a member of the DEAD box family of RNA helicase. p68 RNA helicase plays a very important role in cell proliferation and early organ development and maturation. The expression of the protein was shown to correlate with tumor progression and transformation. p68 can also function as a co-activator for transcription factors such as estrogen receptor alpha, tumor suppressor p53 and beta-catenin (through which cyclin D1, c-jun and c-myc induction is observed). More than that, post-translational modification of p68 including phosphorylation, acetylation, sumoylation, and ubiquitylation can regulate the coactivation effect. Furthermore, aberrant expression of p68 in cancers highlights that p68 plays an important role for tumorgenesis and development.
The expression of p68 (and p72) strongly increases in the polyp to adenoma to adenocarcinoma transition of colon cancer.
Supinoxin is a quinoxalinyl-piperazine compound that is currently in a Phase I dose finding study in patients with advanced malignancies.
RX-3117
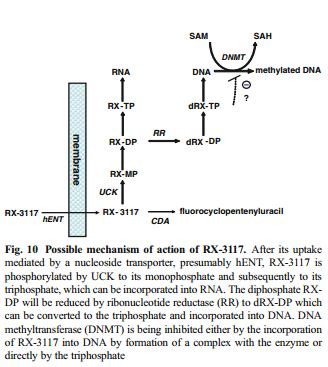
This compound is in an inactive prodrug nucleoside (fluorocyclopentenylcytosine) that becomes activated when acted upon by UCK2, and enzyme that is over-expressed in malignant cells. UCK2 is a pyrimidine ribonucleoside kinase – uridine-cytidine kinase-2. It catalyzes phosphorylation of uridine and cytidine to uridine monophosphate (UMP) and cytidine monophosphate (CMP), respectively. Phosphorylated RX-3117 becomes incorporated into DNA and RNA causing apoptotic cell death.
Phosphorylated 3117 induces apoptotic cell death of tumor cells. UCK is overexpressed in multiple human tumors, but has a very limited presence in normal tissues. The expression profile of UCK2 confers greater specificity to 3117 than gemcitabine, for example, which is activated by the enzyme DCK, a kinase that is highly expressed in both cancer cell and in normal healthy tissue leading to significant toxicities at therapeutic doses.
RX-3117 also mediates the downregulation of DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1), which is an enzyme responsible for the methylation of cytosine residues on newly synthesized DNA and is also a key target for anti-cancer therapies.
Investigational New Drugs [Invest New Drugs] 2013 Dec; Vol. 31 (6), pp. 1444-57. Date of Electronic Publication: 2013 Sep 19
hjhj