ProNai Therapeutics is a Canadian biotech company that recently licensed the rights to a small molecule inhibitor of Cdc7 (cell division cycle 7), a key regulator of both DNA replication and DNA damage response. The drug has shown activity against several cancers in preclinical studies.
Cdc7 in DNA Replication
Cdc7 is a component of DDK (Dbf4-dependent kinase), which phosphorylates MCM (mini-chromosome maintenance) helicase Mcm2-7 after it is loaded onto DNA. Dbf4 is also known as ASK.
The initiation of DNA replication is temporally divided into two phases during the cell cycle. First, an inactive form of the replicative MCM (mini-chromosome maintenance) helicase is loaded onto origin DNA in G1 phase and then activated upon entry into and during S phase by two sets of kinases: cyclin-dependent kinase and Dbf4-dependent kinase (DDK). DDK is a two-subunit Ser/Thr kinase composed of the Cdc7 kinase and Dbf4 regulatory subunits. DDK mediated phosphorylation of the six-subunit Mcm2-7 (MCM) helicase is thought to bring about a conformational change in its structure leading to helicase activation.
If MCM is not phosphorylated, the ATM/ATR-mediated DNA checkpoint control triggers p53 induced cell cycle delay via p21 induction.
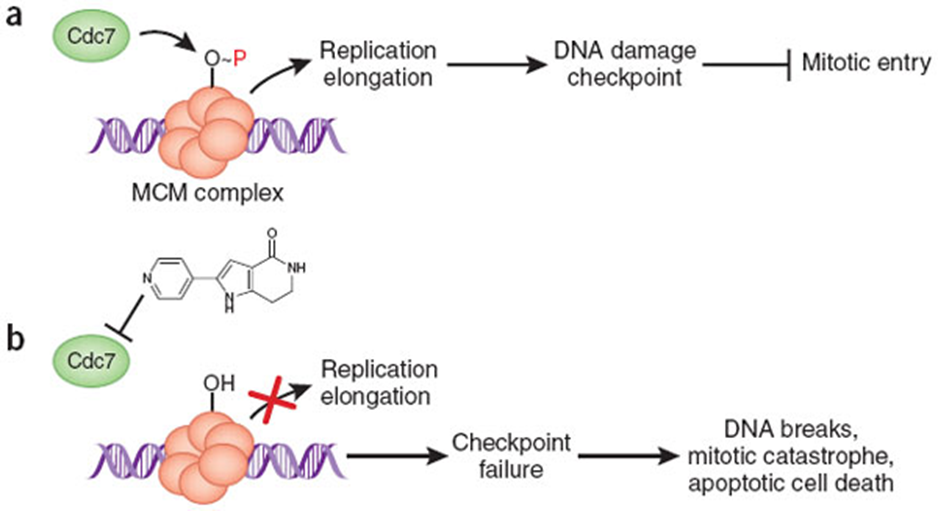
– (a) Cdc7 kinase phosphorylates the MCM complex to stimulate DNA unwinding and activation of DNA polymerases. Sensing of ongoing DNA replication itself is important for activating the DNA damage checkpoint and preventing mitotic entry. (b) Inhibition of the Cdc7 kinase blocks replication initiation, causing failure of the checkpoint and triggering of mitotic failures and apoptotic cell death. http://www.nature.com/nchembio/journal/v4/n6/fig_tab/nchembio0608-331_F1.html
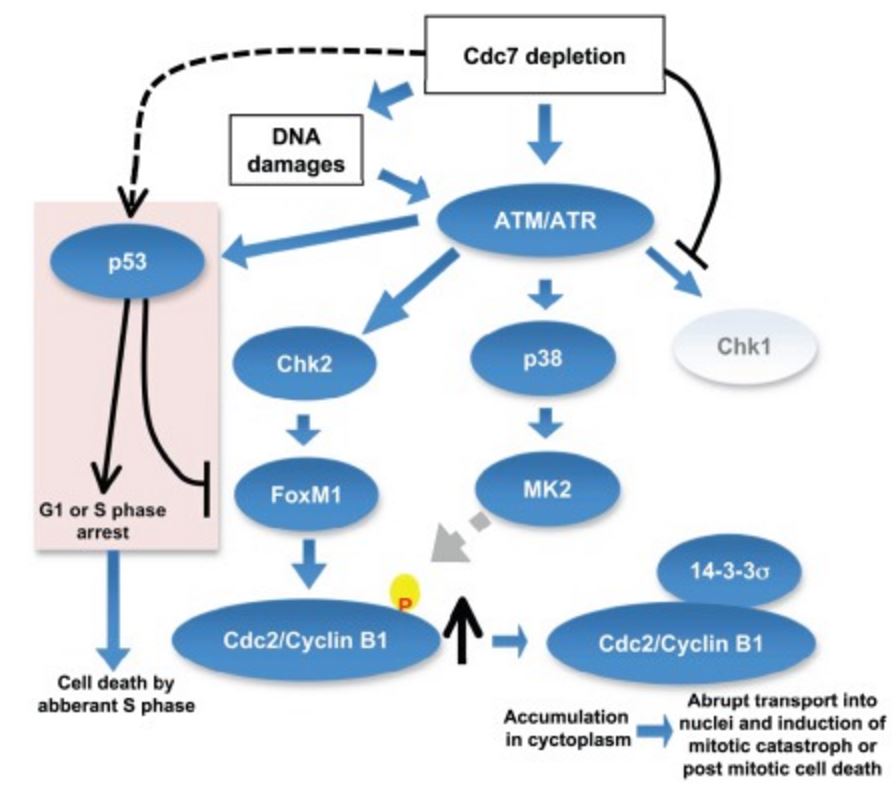
Inhibition of initiation of DNA replication by suppression of Cdc7 kinase leads to activation of ATM/ATR, which may result in the activation of three checkpoint kinases, Chk1, MK2, and Chk2. Since Cdc7 is actively required for activation of Chk1 Chk1 is not activated under this condition. Activated MK2 may phosphorylate Cdc2/Cyclin B1, which in turn may be recognized and bound by 14-3-3σ protein and is sequestered in cytoplasm. Cdc7 depletion can induce DNA damages in cancer cells and activated Chk2 would stabilize the FoxM1 transcription factor, which would induce the expression of CyclinB1. The accumulated CyclinB1 protein is abruptly transported into nuclei and mitotic catastrophe or post-mitotic cell death is induced. In p53-positive cancer cells, p53, activated through ATM/ATR, would induce G1 delay as well as S phase delay possibly through induction of p21. p53 inhibits transcription of FoxM1, thus preventing the induction of Cyclin B1. However, aberrant S phase progression in the absence of Cdc7 would induce cell death in p53-positive cancer cells. https://www.researchgate.net/figure/224934072_fig10_Inhibition-of-initiation-of-DNA-replication-by-suppression-of-Cdc7-kinase-leads-to
Cdc7 in Replicative Stress
Cdc7 also plays an important role in DNA damage response. In cells challenged with hydroxyurea (a ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor needed to produce thymine) and etoposide (a DNA polymerase inhibitor), Cdc7 depletion by small interfering RNA impairs hyper-phosphorylation of Mcm2 at specific Cdc7-dependent phosphorylation sites and drug-induced hyper-phosphorylation of chromatin-bound Mcm4. Furthermore, sustained inhibition of Cdc7 in the presence of these drugs increases cell death supporting the notion that the Cdc7 kinase plays a role in maintaining cell viability during replication stress.
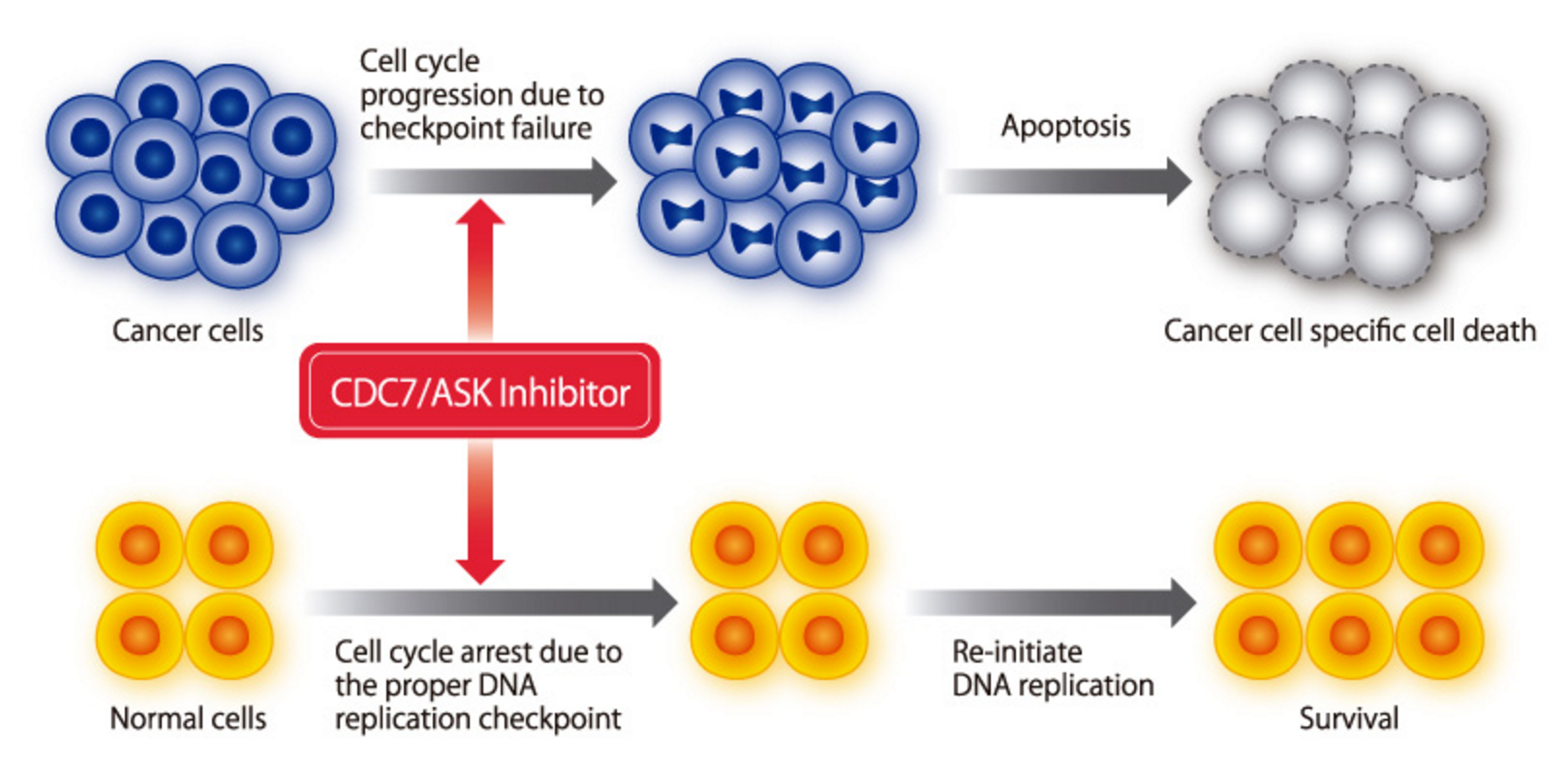
Cdc7 inhibition selectivity induces apoptosis in cancer cells
Cdc7 is over-expressed in many solid and liquid tumors, including triple negative breast cancer. In wild type cells, with proper DNA replication checkpoint control function, Cdc7 depletion causes cell cycle arrest, which reverses later. In cancer cells, with disabled replication checkpoint controls, Cdc7 depletion causes aberrant progression to S and M phase with lethal consequences.
Early stage clinical trials
Millennium Pharmaceuticals is conducting a Phase 1 study of its Cdc7 inhibitor (TAK-931) in patients with advanced non-hematologic malignancies. BMS and Nerviano Medical Sciences terminated two trials of their Cdc7 inhibitors, BMS-863233 and NMS-1116354 , respectively.


No, I don’t. I just saw that the studies listed on http://www.clinicaltrials.gov were terminated.
do you know why BMS/Nerviano terminated the trials of their CDC7 inhibitors?