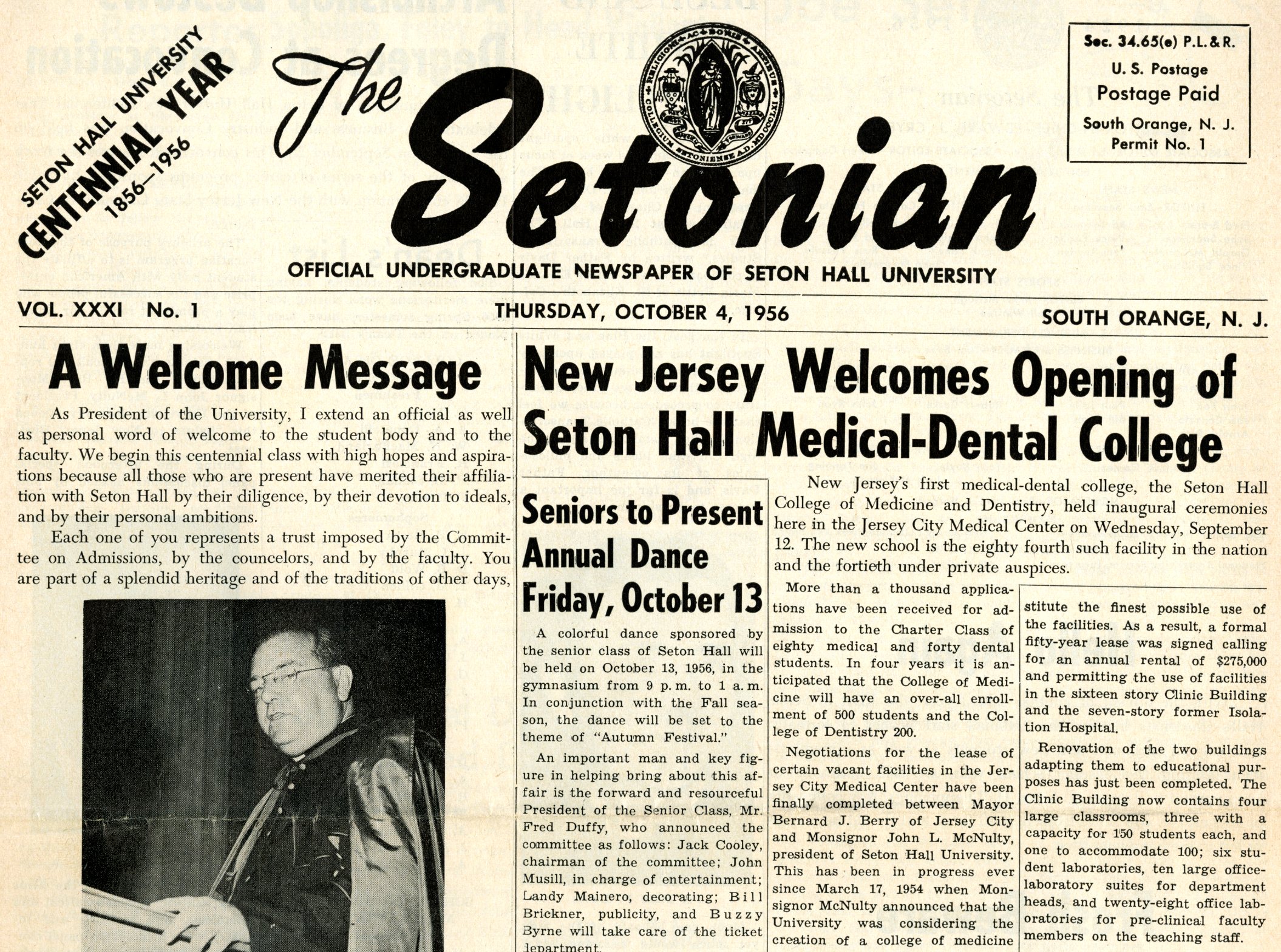
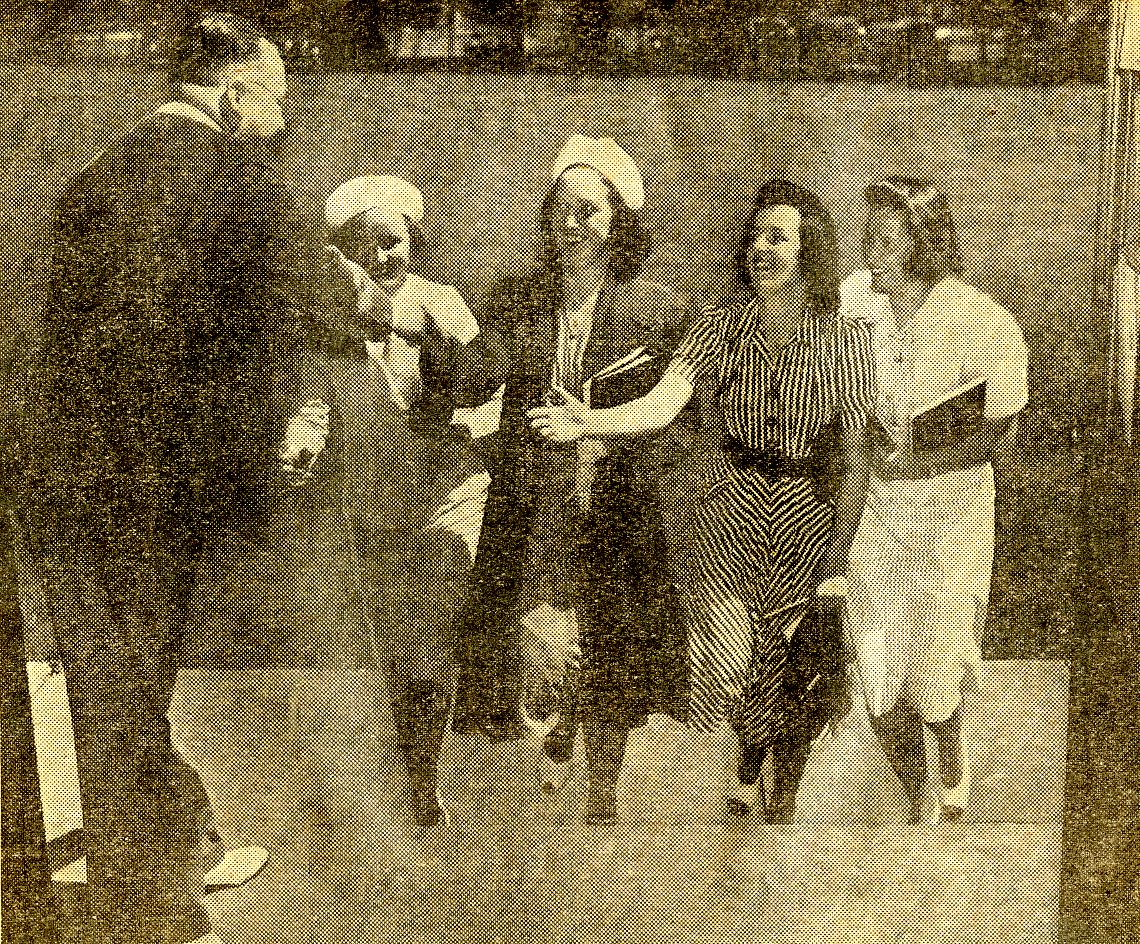 This year marks the 80th anniversary since Women first attended lectures or taught courses at Seton Hall. These trailblazers were part of the now defunct Urban Division established by then College President Monsignor James F. Kelley who provided a more inclusive educational experience for all qualified applicants. Women became a fixture in the classroom from the start of the Spring 1937 semester onward at the extension schools in Newark or Jersey City. In addition, students could opt to attend Summer School on the South Orange campus which served as a prelude to full Co-Education that began here in 1968 and has grown ever stronger to this day. This exhibit showcases documentation from the Seton Hall University Archives & Special Collections Center in order to show the historical evolution and contributions made by the Women of Setonia from its origins onward.
This year marks the 80th anniversary since Women first attended lectures or taught courses at Seton Hall. These trailblazers were part of the now defunct Urban Division established by then College President Monsignor James F. Kelley who provided a more inclusive educational experience for all qualified applicants. Women became a fixture in the classroom from the start of the Spring 1937 semester onward at the extension schools in Newark or Jersey City. In addition, students could opt to attend Summer School on the South Orange campus which served as a prelude to full Co-Education that began here in 1968 and has grown ever stronger to this day. This exhibit showcases documentation from the Seton Hall University Archives & Special Collections Center in order to show the historical evolution and contributions made by the Women of Setonia from its origins onward.
This new Extension Division was conducted under the provisions of the original Seton Hall College Charter of 1861. From here, the first catalog(ue) and press coverage came soon thereafter to provide details of the educational plan that awaited the 321 new students and recently hired faculty that included Professors Blanche Mary Kelly (English), Dorothy I. Mulgrave (English), Mary C. Powers (History), and Aileen Reilly (English) among other instructors hired by the school. Mary Grace Dougherty was the first acknowledged co-ed, but she shared this distinction with others who attended the Newark (St. Patrick’s School) during the Spring of 1937. This also included those who enrolled at the Summer School held in South Orange and/or those on site in both Newark or Jersey City (St. John’s School) from the Fall of 1937 over the next few decades. The first graduates of the Urban  Division were recognized during commencement exercises held in June of 1938. Counted among those who received diplomas at this ceremony include: Virginia Farrell (Hoboken), Gertrude Isaacson (Bayonne), Catherine Netzel (Irvington), and Rita Murphy (Jersey City) [Pictured on the Right] who went on to be connected to Seton Hall for many years to come.
Division were recognized during commencement exercises held in June of 1938. Counted among those who received diplomas at this ceremony include: Virginia Farrell (Hoboken), Gertrude Isaacson (Bayonne), Catherine Netzel (Irvington), and Rita Murphy (Jersey City) [Pictured on the Right] who went on to be connected to Seton Hall for many years to come.
Women continued to succeed in the Urban Division through the 1940s-1960s in a wide range of fields from Academics to Nursing to Law and others. Co-Education came in full to the South Orange campus in 1968 and from this point onward success has been proven through the student body, faculty, administrators, and alumni who have contributed to the benefit of the Seton Hall University community continue to make a difference. The full exhibit will be on view in the Archives & Special Collections Center Reading Room from January-March, 2017. For more information please feel free to contact Alan Delozier, University Archivist via e-mail at: <Alan.Delozier@shu.edu> or by phone: (973) 275-2378