OncoMed is developing several compounds that target Wnt and Notch pathways, which are important in cancer and cancer stem cell maintenance, survival, and proliferation. Biomarkers for response of Her-2-negative breast cancer and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) following treatment with Vantictumab, anti-Wnt monoclonal antibody, have been developed.
Vantictumab is a fully human IgG2 monoclonal antibody that binds to and inhibits Frizzled 7, a transmembrane receptor protein that contains an N-terminal signal sequence, 10 cysteine residues typical of the cysteine-rich extracellular domain of Fz family members, 7 putative transmembrane domains, and an intracellular C-terminal tail with a PDZ domain-binding motif.
Her-2(-) Breast Cancer
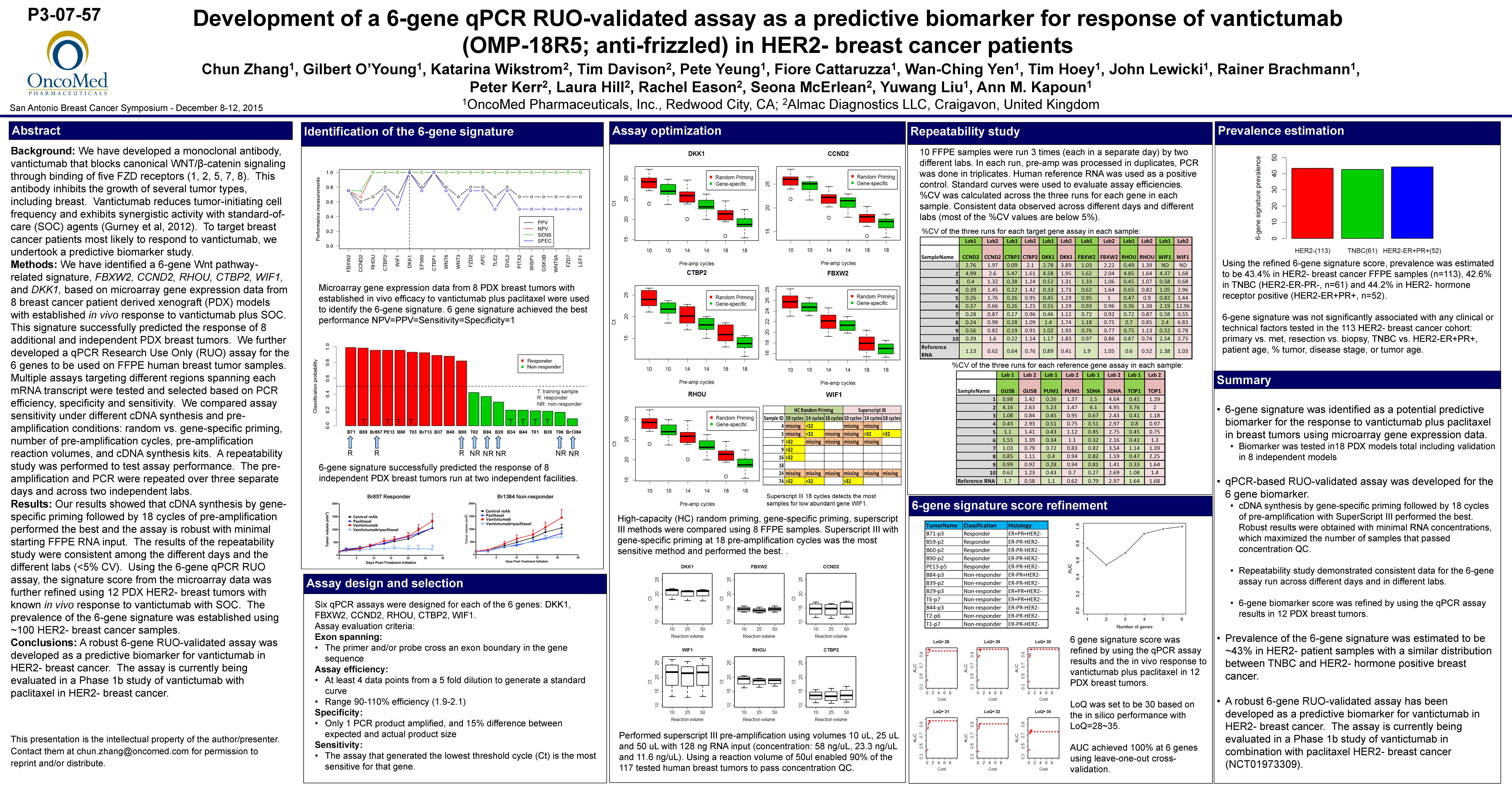
The company identified a 6-gene Wnt pathway related signature based on microarray gene expression data from 8 breast cancer patient derived xenograft (PDX) models with established in vivo response to vantictumab plus standard of care (SOC):
- FBXW2 – F-box proteins are an expanding family of eukaryotic proteins characterized by an approximately 40 amino acid motif, the F box. Some F-box proteins have been shown to be critical for the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of cellular regulatory proteins. In fact, F-box proteins are one of the four subunits of ubiquitin protein ligases, called SCFs. SCF ligases bring ubiquitin conjugating enzymes to substrates that are specifically recruited by the different F-box proteins. Mammalian F-box proteins are classified into three groups based on the presence of either WD-40 repeats, leucine-rich repeats, or the presence or absence of other protein-protein interacting domains. This gene encodes the second identified member of the F-box gene family and contains multiple WD-40 repeats.
- CCND2 – the protein encoded by this gene belongs to the highly conserved cyclin family, whose members are characterized by a dramatic periodicity in protein abundance through the cell cycle. Cyclins function as regulators of CDK kinases. Different cyclins exhibit distinct expression and degradation patterns which contribute to the temporal coordination of each mitotic event. This cyclin forms a complex with CDK4 or CDK6 and functions as a regulatory subunit of the complex, whose activity is required for cell cycle G1/S transition. This protein has been shown to interact with and be involved in the phosphorylation of tumor suppressor protein Rb. Knockout studies of the homologous gene in mouse suggest the essential roles of this gene in ovarian granulosa and germ cell proliferation. High level expression of this gene was observed in ovarian and testicular tumors. Mutations in this gene are associated with megalencephaly-polymicrogyria-polydactyly-hydrocephalus syndrome 3 (MPPH3)
- RHOU – this gene encodes a member of the Rho family of GTPases. This protein can activate PAK1 and JNK1, and can induce filopodium formation and stress fiber dissolution. It may also mediate the effects of WNT1 signaling in the regulation of cell morphology, cytoskeletal organization, and cell proliferation. A non-coding transcript variant of this gene results from naturally occurring read-through transcription between this locus and the neighboring DUSP5P (dual specificity phosphatase 5 pseudogene) locus.
- CTBP2 – this gene produces alternative transcripts encoding two distinct proteins. One protein is a transcriptional repressor, while the other isoform is a major component of specialized synapses known as synaptic ribbons. Both proteins contain a NAD+ binding domain similar to NAD+-dependent 2-hydroxyacid dehydrogenases. A portion of the 3′ untranslated region was used to map this gene to chromosome 21q21.3; however, it was noted that similar loci elsewhere in the genome are likely. Blast analysis shows that this gene is present on chromosome 10. Several transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been found for this gene.
- WIF1 – the protein encoded by this gene functions to inhibit WNT proteins, which are extracellular signaling molecules that play a role in embryonic development. This protein contains a WNT inhibitory factor (WIF) domain and five epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domains, and is thought to be involved in mesoderm segmentation. This gene functions as a tumor suppressor gene, and has been found to be epigenetically silenced in various cancers.
- DKK1 – this gene encodes a protein that is a member of the dickkopf family. It is a secreted protein with two cysteine rich regions and is involved in embryonic development through its inhibition of the WNT signaling pathway. Elevated levels of DKK1 in bone marrow plasma and peripheral blood is associated with the presence of osteolytic bone lesions in patients with multiple myeloma.
This signature successfully predicted the response of 8 additional and independent (PDX) breast tumors. Using the 6-gene qPCR RUO (research use only) assay, the signature score from the microarray data was further refined using 12 PDX HER2- breast tumors with known in vivo response to vantictumab with SOC. The prevalence of the 6-gene signature was established using ~100 HER2- breast cancer samples. A robust 6-gene RUO-validated assay was developed as a predictive biomarker for vantictumab in HER2- breast cancer.
The assay is currently being evaluated in a Phase 1b study of vantictumab with paclitaxel in HER2- breast cancer
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
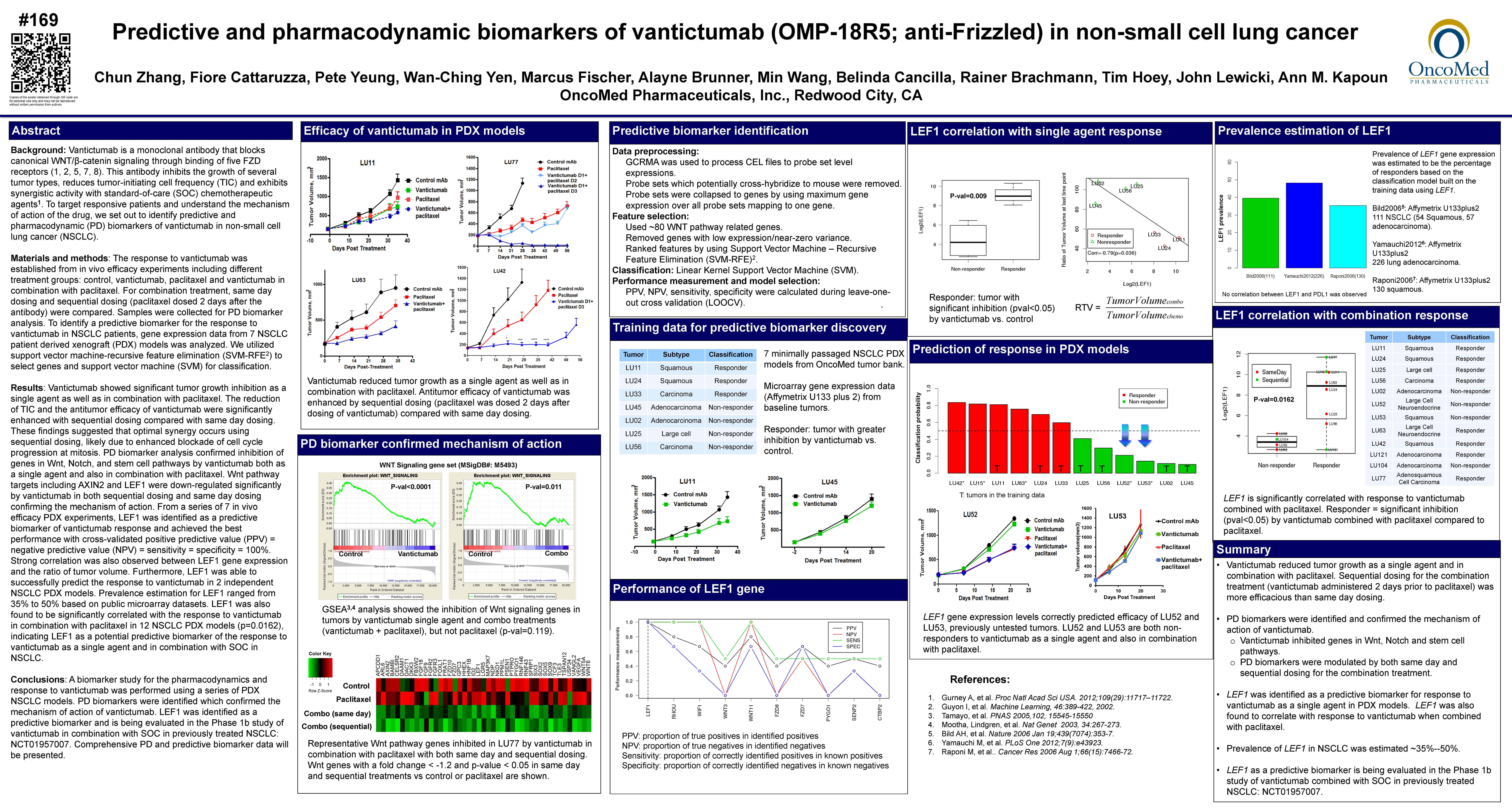
In another pre-clinical study of vantictumab and paclitaxel in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), Wnt pathway targets including AXIN2 and LEF1 were down-regulated significantly by vantictumab in both sequential dosing and same day dosing with paclitaxel, confirming the mechanism of action. From a series of 7 in vivo efficacy PDX experiments, LEF1 was identified as a predictive biomarker of vantictumab response and achieved the best performance with cross-validated positive predictive value (PPV) = negative predictive value (NPV) = sensitivity = specificity = 100%. Strong correlation was also observed between LEF1 gene expression and the ratio of tumor volume. Furthermore, LEF1 was able to successfully predict the response to vantictumab in 2 independent NSCLC PDX models. Prevalence estimation for LEF1 ranged from 35% to 50% based on public microarray datasets. LEF1 was also found to be significantly correlated with the response to vantictumab in combination with paclitaxel in 12 NSCLC PDX models (p=0.0162), indicating LEF1 as a potential predictive biomarker of the response to vantictumab as a single agent and in combination with SOC in NSCLC.
LEF1 is being evaluated in the Phase 1b study of vantictumab in combination with SOC in previously treated NSCLC. This gene encodes a transcription factor belonging to a family of proteins that share homology with the high mobility group protein-1. The protein encoded by this gene can bind to a functionally important site in the T-cell receptor-alpha enhancer, thereby conferring maximal enhancer activity. This transcription factor is involved in the Wnt signaling pathway, and it may function in hair cell differentiation and follicle morphogenesis. Mutations in this gene have been found in somatic sebaceous tumors. This gene has also been linked to other cancers, including androgen-independent prostate cancer. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants.
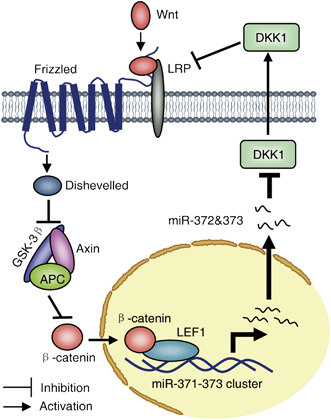
A scheme showing an oncogenic regulatory feedback loop between miR-372&373 and the Wnt/β-catenin-signaling pathway. The miR-371-373 cluster of miRNAs is transcriptionally activated by β-catenin/LEF1 and miR-372&373 represses the DKK1 protein (perhaps TGFBR2, BTG1 and LEFTY1, in addition), which serves as a key antagonist of Wnt/β-catenin signaling, thereby further modulating the Wnt/β-catenin-signaling pathway. http://www.nature.com/onc/journal/v31/n24/fig_tab/onc2011461f6.html


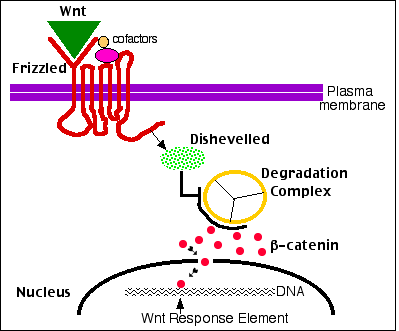
What are the off target effects? Wnt1 is involved in the development of female organs, so it I understand its role in breast cancer development. Unless Wnt1 signaling in lung tissue is an off target, what is its role in normal conditions?