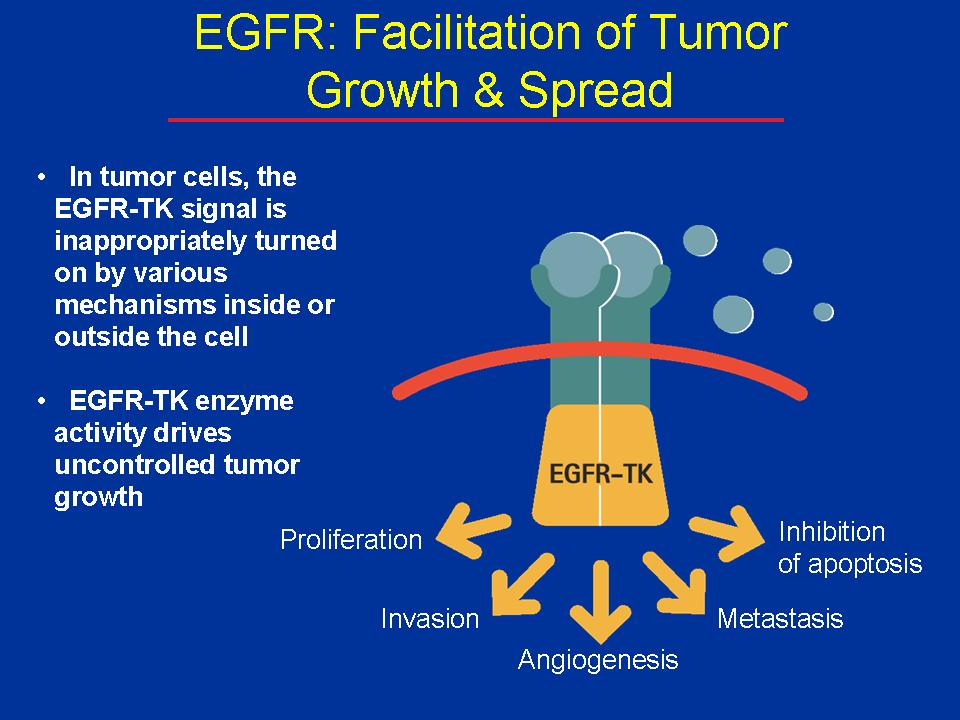
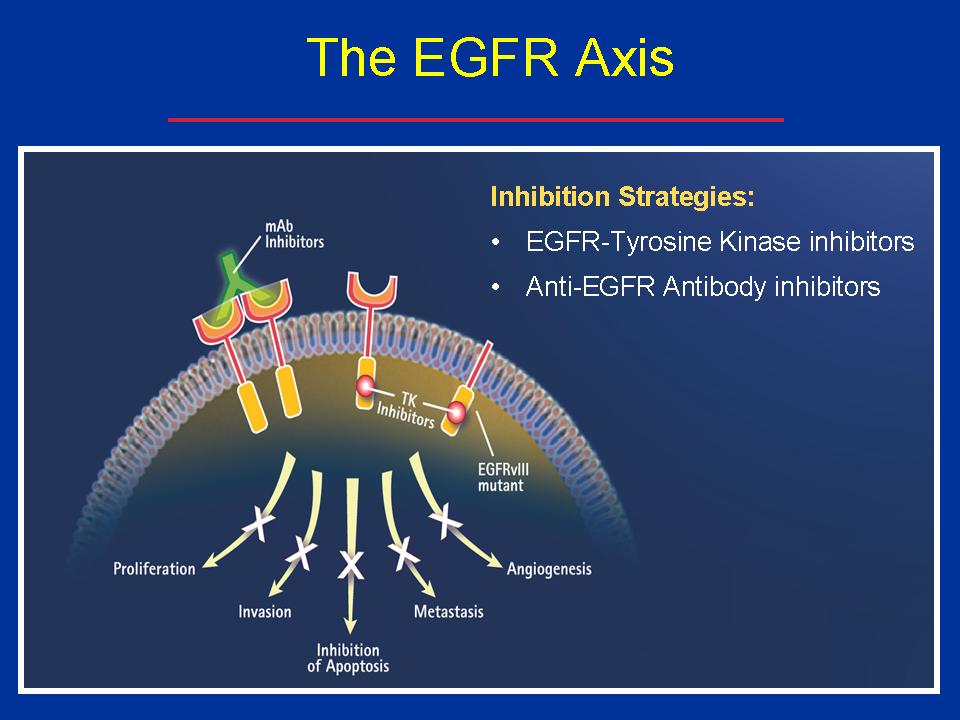
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) receives signals from outside the cell that promote cell division and block apoptosis, leading to proliferation, invasion, and metastasis.
Drugs that inhibit EGFR, which can be antibodies that block EGFR on the outside of the cell (e.g., Erbitux – cetuximab, and Vectabix – panitumumab) or tyrosine kinase inhibitors (e.g., Iressa and Tarceva) that act on the inside of the cell on the cytoplasmic end of the receptor, block the cancer-promoting effects of an activated EGFR molecule.
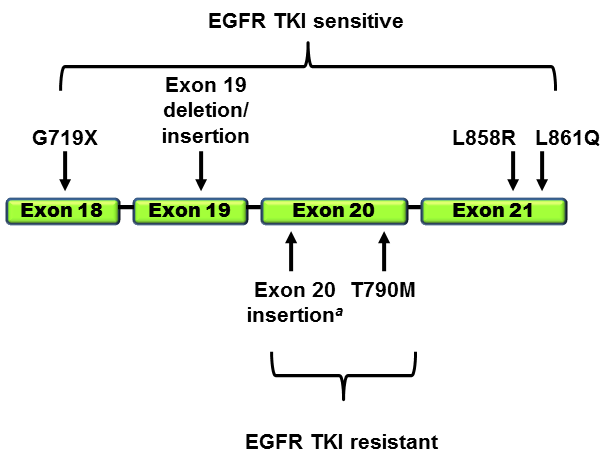
Constitutive Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor expression is common in patients with adenocarcinoma of the lung. While monoclonal antibodies (Erbitux and Vectibix) block binding of ligands that bind to the EGFR receptor, they are not effective when mutations that cause constitutive firing of the receptor emerge. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (Iressa – gefitinib, and Tarceva – erlotinib) have provided effective treatment of patients with mutations leading to constitutive activity of the EGFR receptor.
However, patients receiving tyrosine kinase inhibitors become resistant to therapy, principally due to the T790 mutation of the EGFR. The T790M mutation can be detected as a “second-site mutation” in more than 50% of EGFR-mutated lung cancers that have developed acquired resistance to erlotinib or gefitinib (Kobayashi et al. 2005; Pao et al. 2005).
Clovis Oncology has developed an EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor that targets the T790 mutation called rociletinib (CO-1686). T790M is rarely (<5%) found in untreated EGFR-mutated tumors. In approximately half of patients with baseline T790M mutations in their lung cancer, the T790M may be present as an underlying germline mutation. These germline T790M mutations occur infrequently (~0.5% of never smokers with lung cancer; Girard et al. 2010) and may be associated in some instances with familial cancer syndromes (Bell et al. 2005). AstraZeneca is also developing an inhibitor of the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor with the T970m mutation.
Clovis started its rolling NDA submission – at the 500 mg twice daily dose, the overall response rate was 60% and the disease control rate was 90%. An active metabolite of rociletinib, M502, inhibits IGF1-R/IR (insulin receptor), which leads to insulin resistance; this is why grade three/four (of four) hyperglycemia occurred in 17% of patients.
A number of clinical trials continue to assess rociletinib for patients with NSCLC. The phase II/III TIGER 1 trial is comparing rociletinib with erlotinib as first-line therapy in treatment-naïve patients with EGFR mutations who have not been screened for T790M status. TIGER 2, a single-arm phase II trial, is evaluating rociletinib as second-line therapy in patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC who are T790M-positive. The randomized phase III TIGER 3 trial is evaluating rociletinib versus chemotherapy in patients who have progressed on a first-line EGFR TKI and are also T790M-positive.
In addition to monotherapy trials, multiple trials are planned to assess rociletinib in combination with other therapies. Studies looking at rociletinib with inhibitors of PD-L1, PD-1, and MEK are anticipated to begin enrolling patients in the second half of 2015.