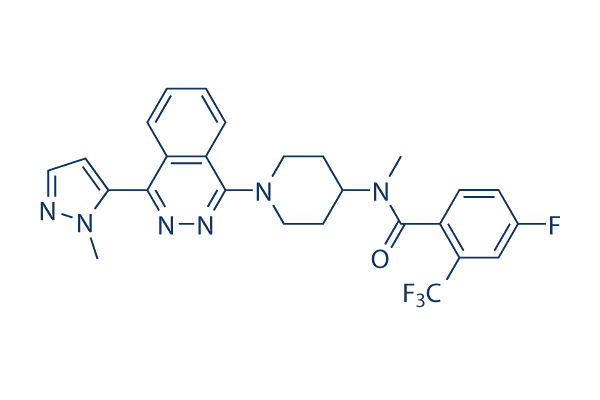
Eli Lilly has licensed exclusive worldwide rights to Ignyta’s Phase I taladegib oncology development program, in a deal the San Diego biotech said could generate up to $53 million-plus. Taladegib is an oral bioavailable small molecule hedgehog/smoothened antagonist. The compound has achieved clinical proof-of-concept and a recommended Phase II dose based on earlier clinical studies.
Ignyta said it also licensed Lilly to exclusive worldwide rights to the topical formulation of taladegib, a late preclinical program being developed for patients with superficial and nodular basal cell carcinoma.
Taladegib, LY2940680 (hedgehog/SMO antagonist), is a chemical entity that binds to the human SMO receptor and inhibits Sonic hedgehog-dependent expression of genes.
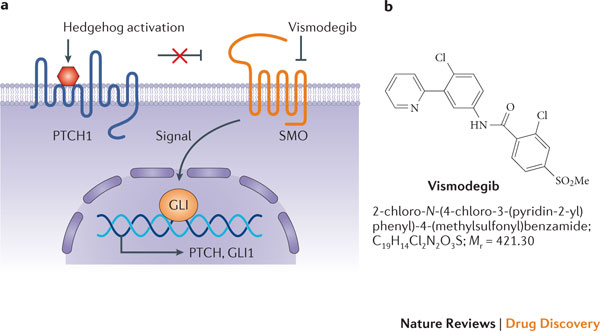
Vismodegib is another hedgehog/SMO antagonist that is approved as Erivedge, a prescription medicine used to treat adults with a type of skin cancer, called basal cell carcinoma, that has spread to other parts of the body or that has come back after surgery or that your healthcare provider decides cannot be treated with surgery or radiation.
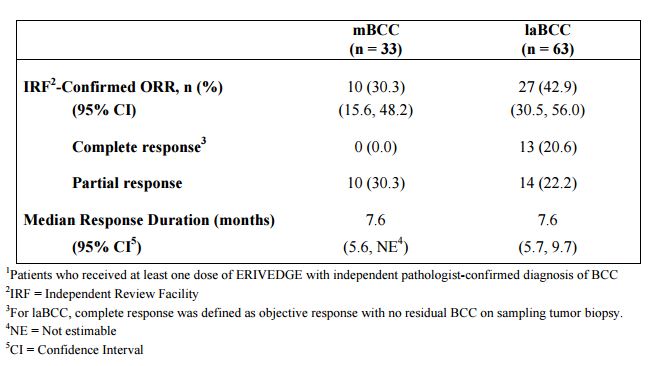
In clinical studies, Erivedge was shown to have an objective response rate for metastatic and locally advanced basal cell carcinoma of the skin of 30% and 42%, respectively, with complete disappearance of locally advanced disease in half of the responders. The median duration of response in both groups was 7.6 months.
The Hedgehog pathway is a unique signaling system. Normally, Smoothened (SMO) is functionally inert (left) being confined by Patched (12 membrane-spanning receptor protein) in cytoplasmic vesicles. This sequestration seems to depend on the catalytic actions of Patched on Smoothened, which prevents Smoothened from moving into primary cilia. Under these conditions, Gli (red) is cleaved into a protein that moves to the nucleus, where it operates as a transcriptional repressor. However, when Hedgehog ligand (right) binds to Patched, the latter release Smoothened from its site of sequestration, and Smoothened moves onto the surface of the primary cilium and proceeds (in some unknown fashion) to prevent cleavage of Gli, enabling uncleaved Gli to move to the nucleus where it acts as an inducer of transcription.
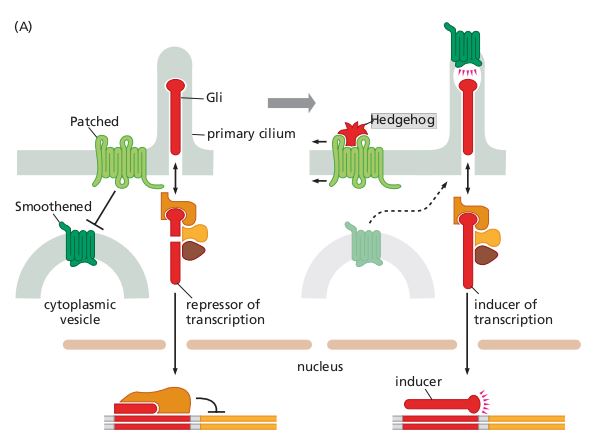
Copyright 2014 from The Biology of Cancer, 2nd Ed. by Weinberg. Reproduced by permission of Garland Science/Taylor & Francis LLC.
Vismodegib (Erivedge) interferes with the Hedgehog pathway. The Patched (12 membrane-spanning receptor protein) normally disables Smoothened (7 membrane-spanning protein) rendering it functionally inert. This maintains transcription factor Gli in a cleaved state, acting as a transcriptional repressor. When Hedgehog proteins bind to Patched, Smoothened is released and protects Gli from cleavage. Uncleaved Gli travels to the nucleus and is an inducer of transcription, increasing Cyclin D1 and stimulating the cell cycle (proliferation). Vismodegib blocks the actions of Smoothened. It is administered orally in 150 mg capsules.
Taladegib inhibits cancer growth in cell lines containing a mutation in the gene encoding Smoothened that researchers had previously observed in patient with cancer who developed resistance to vismodegib. Taladegib binds to the Smoothened (Smo) receptor and potently inhibits Hedgehog (Hh) signaling.
Taladegib is also in clinical studies for the treatment of esophageal cancer in combination with paclitaxel, carboplatin and radiation therapy.

Great insight, keep it up.