In a Phase 3 study of 929 patients with previously treated multiple myeloma, two proteasome inhibitors, Velcade (bortexomib – Johnson & Johnson and Takeda) ) and Kyprolis (carfilzomib – Amgen), in combination with dexamethasone, were compared. Patients treated with Kyprolis had a median progression-free survival of 18.7 months, versus 9.4 months for those treated with Velcade.
These are the results of the interim analysis of the ENDEAVOR trial – patients continue to be followed. In addition, Kyprolis demonstrated “superiority” over Velcade for secondary objectives of higher overall response rate and lower neuropathy events.
Overall survival data are not yet mature, and Sean Harper, Amgen’s head of R&D, said the study will continue until overall survival can be determined. Results from the head-to-head CLARION trial comparing Kyprolis to Velcade in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients are expected in 2016.
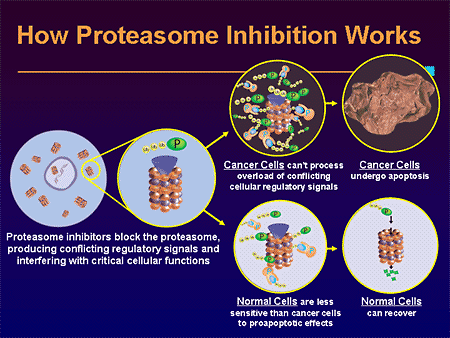
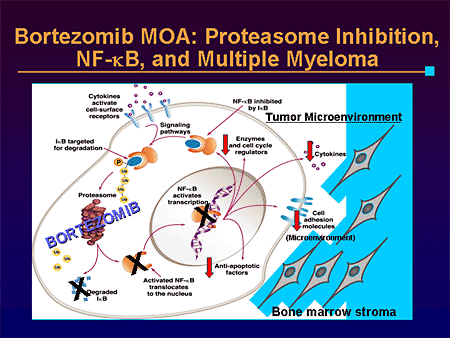
Both drugs belong to the proteasome inhibitor class, which work by inhibiting the digestion of proteins inside the cell. Blocking the degradation of cell cycle regulatory proteins via disruption of the ubiquitin/proteasome system is an important mechanism. In multiple myeloma, antibody molecules are synthesized at a high rate, which increases the rate of production of misfolded proteins. If proteasome function is blocked, the build-up of these proteins triggers apoptosis. In addition, proteasome inhibition blocks the NFkB pathway by inhibiting the degradation of IkB, which blocks NFkB from translocating to the nucleus. In multiple myeloma, NFkB signaling controls VEGF and adhesion molecule regulation; adhesion molecules are critical in multiple myeloma because adherence to bone marrow stem cells is required for heterotypic cellular interactions.
Proteins are targeted for recognition and for subsequent degradation by the proteasome via the attachment of multiple ubiquitin molecules. The 26S proteasome is a 2,000 kDa multisubunit cylindrical complex comprised of a 20S core catalytic component (the 20S proteasome) capped at one or both ends by a 19S regulatory component (Figure 1)(Adams, 2003). The 19S subunit recognizes and binds the polyubiquitinated protein and cleaves the ubiquitin chain from the protein substrate. The protein is then unfolded and fed into the 20S core, and the ubiquitin molecules are recycled. The 20S core is composed of 4 stacked rings: 2 outer rings (α rings) and 2 internal rings, termed β rings, in which proteolysis occurs. Each β ring consists of 7 subunits containing 3 active enzymatic sites termed trypsin-like, chymotrypsin-like, and post-glutamyl peptide hydrolase-like (caspase-like), after enzymes that show similar activity or specificity Almond and Cohen 2002 and Adams 2003. Within the 20S core, proteins are progressively degraded to small, 3- to 25-amino-acid peptides (Nussbaum et al., 1998).
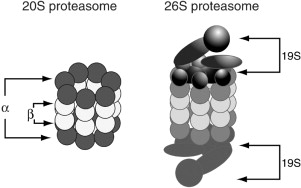
A schematic of the 26S proteasome The 26S proteasome, a 2,000 kDa multiprotein complex, is comprised of a proteolytically active 20S core particle that is capped by 1 or 2 19S regulatory particles. The 19S regulatory units recognize ubiquitinated proteins and control access to the proteolytic core. Reprinted from Adams (2003) with permission from Cancer Treatment Reviews.
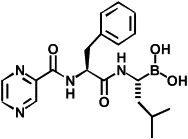
Bortezomib (Velcade) is a small molecule that reversibly binds to the chymotrypsin-like site on the 20S core.
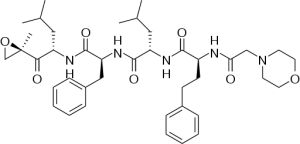
Carfilzombib (Kyprolis) irreversibly binds to the 20S proteasome. It is approved for use in patients who do not respond or have relapsed following treatment with Velcade.
The final results of the ENDEAVOR study are not available yet. On reason for the dratic difference in progression-free survival could be the inclusion of patients who have been previously treated with Velcade. The inclusion criteria of the study state that patients could have received either Velcade or Kyprolis, previously. [Of course, the head to head CLARION study in newly diagnosed patients that is currently ongoing and anticipated to have results in 2016 will be most informative with respect to this rationale.]
The key inclusion criteria of the study with respect to prior treatment include the following:
- Received 1, but no more than 3 prior treatment regimens or lines of therapy for multiple myeloma. (Induction therapy followed by stem cell transplant and consolidation/maintenance therapy will be considered as one line of therapy).
- Prior therapy with Velcade is allowed as long as the patient had at least a PR to prior Velcade therapy, was not removed from Velcade therapy due to toxicity, and will have at least a 6 month Velcade treatment-free interval from last dose received until first study treatment. (Patients may receive maintenance therapy with drugs that are not in the proteasome inhibitor class during this 6 month Velcade treatment-free interval).
- Prior therapy with carfilzomib is allowed as long as the patient had at least a PR to prior carfilzomib therapy, was not removed from carfilzomib therapy due to toxicity, and had at least a 6-month carfilzomib treatment-free interval from last dose received until first study treatment. (Patients may receive maintenance therapy with drugs that are not in the proteasome inhibitor class during this 6 month carfilzomib treatment-free interval). The exception to this is patients randomized or previously randomized in any other Onyx-Sponsored Phase 3 trial.