Finance in the Middle East: The Strategic Power of Sovereign Wealth Funds
Fady Nakhla
Staff Writer
The financial landscape in the Middle East, particularly in countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE, has experienced a transformative shift in recent years. Driving this shift is the region’s powerful Sovereign Wealth Funds (SWFs), such as the Public Investment Fund (PIF) of Saudi Arabia, Abu Dhabi Investment Authority (ADIA), and Mubadala Investment Company in the UAE. These SWFs, backed by vast oil wealth, have become dominant forces in global investment, with significant capital flows directed toward both international and domestic markets.
Record-breaking Investments in Global Markets
In recent years, SWFs in the GCC, especially from Saudi Arabia and the UAE, have deployed billions of dollars in strategic investments across various sectors. In 2022, these funds collectively invested a record $83 billion, targeting industries such as technology, clean energy, infrastructure, and healthcare. This growing influence is supported by the region’s oil revenues, which have enabled these funds to become significant players in international markets.
For example, Saudi Arabia’s PIF signed a landmark $50 billion partnership with Chinese financial institutions in August 2024, further strengthening ties between the two nations. The PIF’s investment strategy aligns with Saudi Vision 2030, a national plan aimed at diversifying the economy away from oil dependency by focusing on sectors such as clean energy, tourism, and entertainment.
SWFs at the Forefront of Mergers and Acquisitions
The role of SWFs in the Middle East is particularly prominent in mergers and acquisitions (M&A). In the first half of 2023, the MENA region saw 318 M&A deals totaling $43.8 billion, with the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries accounting for most of the activity. Notably, the UAE and Saudi Arabia led the way, with the technology sector contributing $15 billion to the total deal volume.
Major deals in 2023 included PIF’s Savvy Games Group acquiring U.S. mobile game developer Scopely for $4.9 billion, while Abu Dhabi Investment Authority (ADIA) and Apollo Global Management announced a plan to acquire UAE-based Univar Solutions for $8.2 billion. These deals reflect the region’s growing influence in international markets, particularly in high-growth sectors like technology and fintech.
Investment in Strategic Sectors
While SWFs are highly active abroad, they are also heavily focused on domestic investments aimed at building national economies. For instance, Saudi Arabia’s PIF has played a pivotal role in the development of the kingdom’s giga-projects such as NEOM and Qiddiya, which are part of Vision 2030’s efforts to diversify the economy. In 2024 alone, PIF invested $10.2 billion globally, while continuing to support local projects, including investments in sectors like electric vehicles, renewables, and sports tourism.
Similarly, Mubadala has been a key player in sectors such as biopharma, technology, and renewable energy, making significant acquisitions in U.S. and European companies. ADIA has also expanded its portfolio with acquisitions in global real estate, technology, and infrastructure.
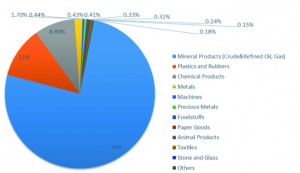
Strategic Partnerships and Global Influence
SWFs from the Middle East are increasingly forming strategic partnerships with global financial institutions and private equity firms to maximize returns and bolster influence. For example, PIF’s partnerships with Chinese tech giants like Alibaba demonstrate its commitment to innovation and future-focused industries.
These funds are not just passive investors; they actively engage in co-investment strategies and partnerships, particularly in markets across Asia, Europe, and North America.
Additionally, the geopolitical influence of these investments cannot be overlooked. The U.S. has expressed concerns over the growing economic ties between Saudi Arabia and China, especially given PIF’s extensive investments in Chinese technology and infrastructure.
The Role of Foreign Banks
The attractiveness of the Middle East as an investment hub has also drawn foreign banks to the region. These banks are eager to tap into the capital flows and lucrative opportunities presented by the region’s vast wealth and strategic projects. The growing presence of foreign financial institutions in Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Qatar is a testament to the region’s increasing importance in global finance.
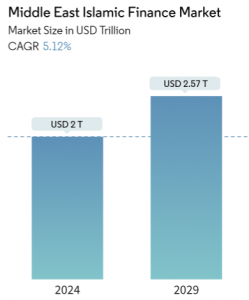
Conclusion
The Middle East’s sovereign wealth funds, particularly PIF, Mubadala, and ADIA, have evolved into powerful players shaping both the regional and global financial landscape. With combined assets exceeding $4 trillion, these funds are not only ensuring long-term wealth creation for their nations but are also contributing to economic diversification, job creation, and geopolitical influence. As they continue to make strategic investments across multiple sectors, GCC sovereign wealth funds are poised to play an even larger role in shaping the global economy in the years to come.
Contact Fady at Fady.Nakhla@student.shu.edu