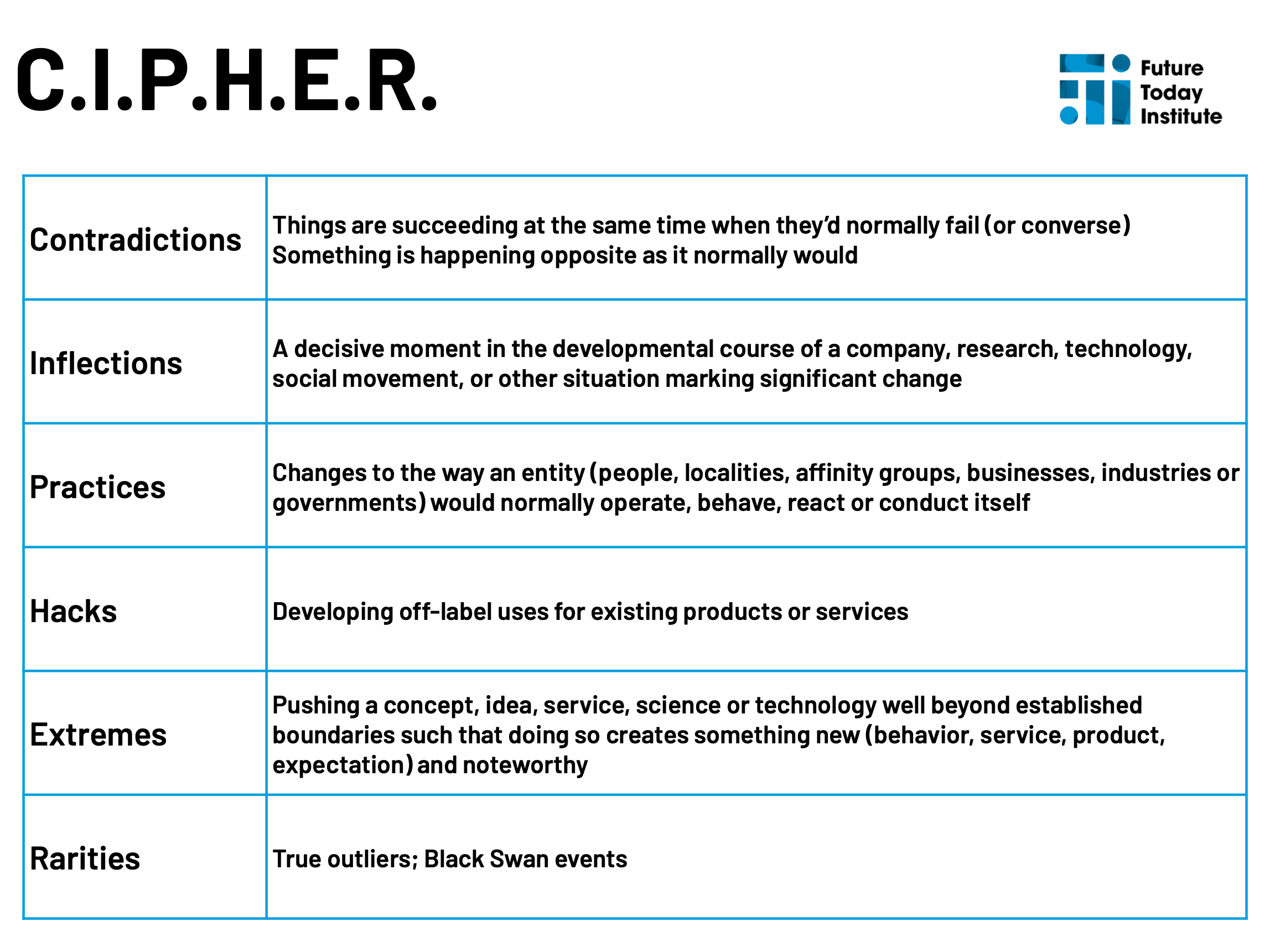
Contradictions
Initially, people might understand that there is a problem when it comes to national security or privacy safety; they believe it is important to take actions for better protection to mitigate future problems from arising. In the effort to fight cybercrimes, individuals lack the tools and education on the subject. They might express their concerns about the welfare of their privacy or the security of their personal information, but they refuse to take any steps to assist in their protection. The main disconnect on the topic of cybersecurity results in the ineffective education placed on the topic, just does not convey the message of immediacy. Additionally, news sources and articles that people chose to look at do not create any sense of awareness on cybersecurity, although good sources remain out there. In the present state of our world, many people choose not to respond to potential threats or future obstacles, but prefer to tackle issues that affect them immediately; individuals refuse to act due to convenience factors. This argument can even be seen as those people still deny the visible effects of climate change. In the future, more education in school systems and even over the news needs to allow for people to become more alert to possible threats that can disturb every part of their lives.
What should be other approaches going forward to establish a better understanding? How can these changes in consciousness result in more solutions? Many countries have to take into consideration the access of their citizens’ data to other nations in the future. This can be seen through the Chinese developed app TikTok. Through this app, the Chinese government can use the complex algorithm to understand users’ preferences and their personal information to gather into files for storage. This additionally goes for other Chinese-owned apps like MoneyGram and Genworth. But, this issue does not just relate to foreign-owned companies, as the United States-based corporations like Meta, Amazon, and Google compile user data and sell it to other companies or individuals.
Contradictions also arise when it comes to the importance of cybersecurity efforts between companies and government agencies. As the United States government continuously is pushing to advance cybersecurity to the future, as seen in the recent approval in the House of the National Cybersecurity Preparedness Consortium Act of 2021, businesses want government actions limited in their operations. Many businesses, especially small businesses, are having trouble allocating funds on the issue of cybersecurity or feel like they do not need any additional protection because of the small scale of their company.
Inflections
As cybersecurity continues to have major disruptive advancements, the most prominent turning point for the matter was the recent war between Russia and Ukraine. The adjustments that Ukrainian citizens had to make in their daily lives became drastic while so many people watched to view the next steps that were taken by both the governments of Russia and Ukraine. The conflict united foreign governments to set sanctions on Russia in the hopes it would end the fighting. With these sanctions creating economic tragedies in Russia, the worry and panic amongst individuals grow as the potential for a cyberattack in retaliation on the United States increases, making economic disaster for the United States as well. Many experts look to increase the utility of different cyber instruments for the enhancement of state power.
What does the war between Russia and Ukraine teach individuals about the future of cybersecurity? It indicates the weakness of many foreign governments. It additionally points out other areas where cybersecurity could be an issue, like in space. Many experts warn of future hacks involving the use of space weapons and cyberwarfare as technology progresses. With the United States developing Space Force and its goals for transformation and modernization, other governments such as Russia and China will attempt to compete in developing space weaponry and militia.
Practices
One of the emerging practices, particularly in the government sector, is the model of zero trust. Governments hope this system in the future allows for the recognition of where these data breaches are coming from, making it easier to stop them from reoccurring. One of the most prominent features of the zero trust model is the concept of recognizing that threats can happen internally or externally. What happens in this area is the limitation of access as the model assumes that a hack has already taken place. Although zero trust is utilized to assist in stopping existing threats due to its way of running, it can be more effective when combined with other forms of preventative software.
Another factor to consider in the space of cybersecurity is the more frequent use of cloud computing as it might offer better protection for individuals and smaller businesses. Although some see the cloud as a great way for hackers to gain data, which is very true, cloud computing offers better security than people initially have due to the existence of cloud vendors. Cloud computing, the internet of things, and cybersecurity are all very closely interconnected, making this practice more popular in recent years; global cloud computing is forecasted to grow by 2025 to over $650 billion.
Hacks
When it comes to cybersecurity attacks, human error is looked at as the main cause; it is estimated in a study by IBM that 95% of breaches occur due to human error. This problem can be evidently due to the misunderstanding of the software allowing hackers to have a gateway to different systems or due to the inability of knowledge and training on cybersecurity. This can result in wrongful actions or no actions at all. The unintended consequences ending in attacks create huge losses, from which many are unable to recover. It is noted that “one in four employees who made cybersecurity mistakes lost their jobs.” Additionally, businesses can experience future financial losses, client losses, and system failures. To mitigate problems resulting from human error in years to come, training and education must be essential.
Extremes
The topics of cybersecurity and cybersecurity attacks are extremes in themselves, with each of their futures becoming more and more drastic as the world’s digital infrastructure matures. Typically, one would identify extremes as a situation that appears to be shocking, but anymore nothing with cybersecurity is truly that shocking. Many people would say that cyber warfare or data breaches would be viewed as extremes, but they are not unanticipated occurrences. Developing a roadmap or utilizing strategic foresight for better planning methods allows for future “extremes” to not appear to be so unrealistic or intense. Looking closer at emerging trends in recent years could allow for some clarification on the distinct realms of cybersecurity.
The combination of surveillance capitalism and cybersecurity especially during the age of Covid-19 is probably the most shocking concept to the international population that has no prior knowledge of either of the topics. These subjects go hand-in-hand as the gain in data allows for governments and businesses to profit off individuals’ personal information. As the popularity of surveillance grows significantly in the East, the West is adopting more models to fit the concerning demand for data. How can this be prevented in the future? The government must not only pass strict laws concerning the privacy of citizens in countries utilizing surveillance but also work towards holding people accountable for their cyber activity. If this does not happen, more and more cyber attacks will cause widespread user information and data leaks, overall resulting in no privacy being attained. This could then result in further mental health problems due to people and their extensive worry about becoming hacked and greater internet safety issues.
Rarities
With all the unexpected outcomes of cybersecurity, many people might be shocked when confronted with the bipartisan agreements in the United States on the topic. This unity is so significant, especially with government involvement in cybersecurity, indicating that more laws and regulations can erupt soon. Here are some recent examples of bipartisan support on the matter of cybersecurity that could overall increase privacy and protection for individuals in the future:
- The Healthcare Cybersecurity Act introduced by United States Senators Bill Cassidy, M.D. (R-LA) and Jacky Rosen (D-NV) exposes the need for better security of data in health facilities and hospitals. The governmental support behind this new act is in response to the 46 million Americans having their health information exposed in 2021.
- Senate members Gary Peters (D-MI) and Rob Portman (R-OH) explained the high level of importance in the legislation that enables “operators to alert the federal government when they are hacked or make a ransomware payment.” On March 15, 2022, President Biden signed it into law as the Cyber Incident Reporting for Critical Infrastructure Act.